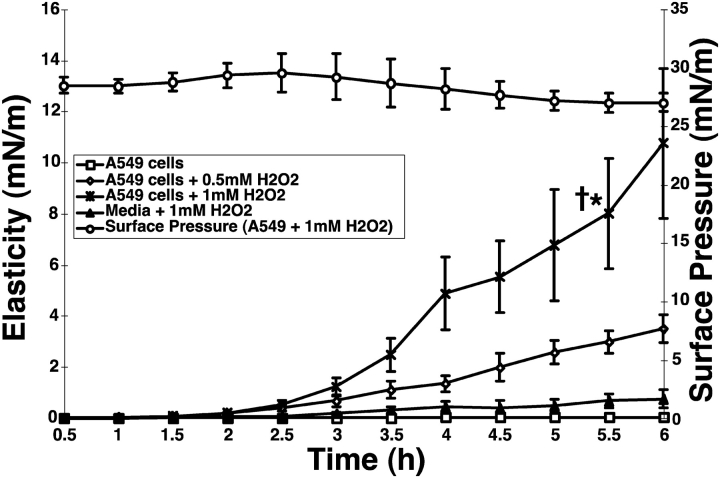
Figure 6.
Dose- and time-dependent increase in surfactant gelation by hydrogen peroxide treatment of A549 AEC. A549 AEC were cultured in 50-mm sterile dishes, and used for rheology studies when 80% confluent. Cells were washed in FBS-free DMEM, placed into the ISR then exposed at time zero to H2O2 (0, 0.5, or 1 mM). A surfactant monolayer was spread on the AEC supernatant, and kinetic measurements of elasticity, Gs', were recorded every 30 min up to 6 h. Surface pressure was continuously monitored with a Wilhemy balance throughout the duration of the experiment (AEC exposed to 1 mM H2O2, open circles). Conditioned supernatant from resting AEC preserves the fluidity of lung surfactant (open squares). Conditioned media from H2O2-treated AEC induces increases in elasticity representing lung surfactant gelation at 5.5 h (open diamonds and stars) (1 mM H2O2-AEC versus resting AEC, *P < 0.005, n = 3; 1 mM H2O2-AEC versus media + 1 mM H2O2, †P < 0.005, n = 3).