Figure 1.
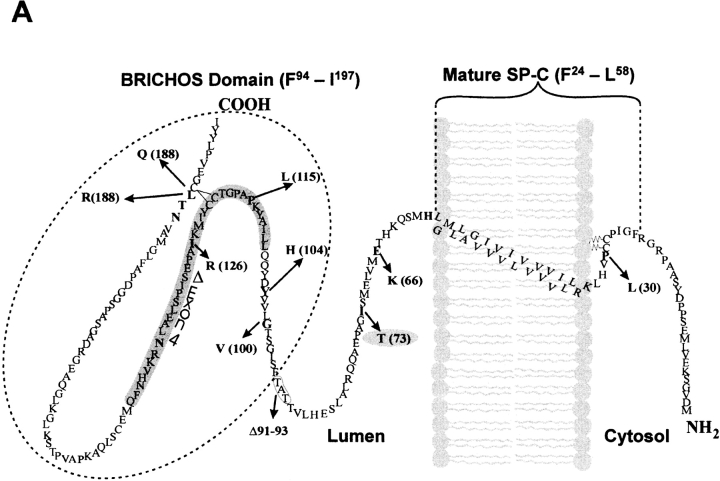
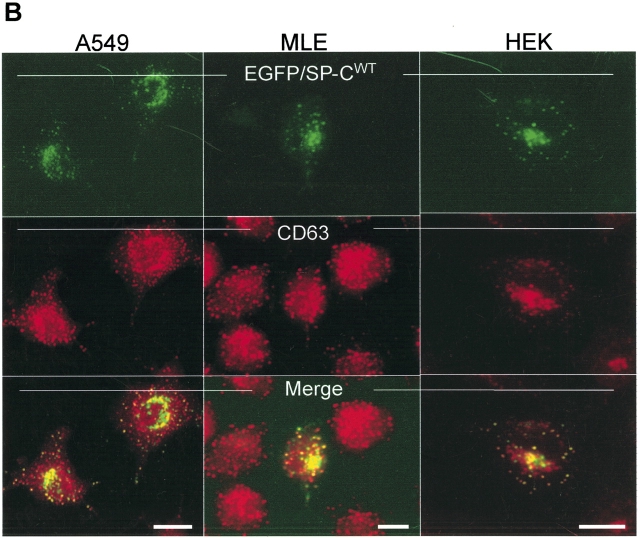
Wild-type SP-C is trafficked to vesicles distal to the Golgi independent of cell type. (A) Amino acid sequence of the human SP-C pro-protein showing cytosolic, transmembrane, luminal, and BRICHOS domains. The secreted mature SP-C, the BRICHOS domain (hatched oval circle), and mutations found in association with ILD are shown. The Δexon 4 BRICHOS domain mutation and a non–BRICHOS domain mutation analyzed in the present study are highlighted in gray. The BRICHOS domain flanks the C-terminal starting at phenylalanine 94. Amino acid nomenclature is based on the published SP-C sequence (31). (B) A549, MLE, and HEK cells transiently transfected with EGFP/SP-CWT (top row) show similarities in vesicular co-localization (bottom row) with Texas Red–conjugated CD63 (middle row) antibody. Bar, 5 μm.