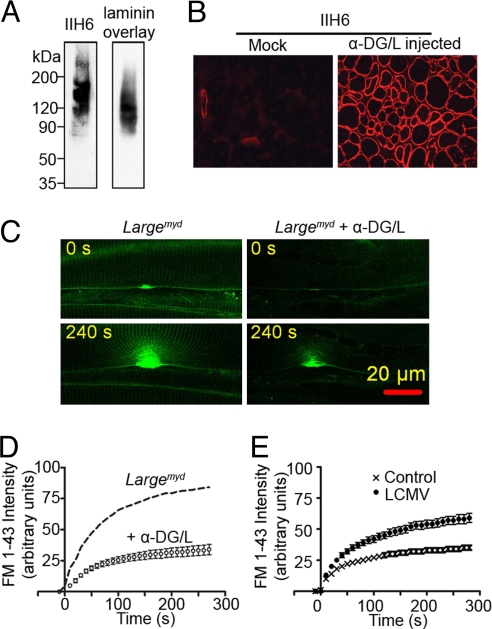
Fig. 5.
Effect of α-DG-mediated association of the basal lamina with the sarcolemma on membrane integrity. (A) The purified recombinant α-DG reacted with the glycosylated α-DG antibody IIH6 (Left) and bound to laminin in the laminin overlay assay (Right). (B) The Largemyd muscles injected with recombinant α-DG/L (α-DG/L injected) or saline (Mock) were stained with IIH6 antibody. (C) Representative micrographs of membrane damage assay performed on Largemyd muscle fibers treated with or without recombinant α-DG/L. (D) Plot of FM 1-43 fluorescence intensity against time of the in situ membrane damage assay in Largemyd muscle fibers treated with recombinant α-DG/L (n = 7). The dash curve represents mean FM 1-43 fluorescence intensity of the membrane damage assay in Largemyd muscle from the Fig. 4E. (E) Plot of FM 1-43 fluorescence intensity against time for the in situ membrane damage assay carried out in C57BL/6 muscle fibers treated with (n = 9) or without (n = 11) LCMV. All of the data are means ± SEM.