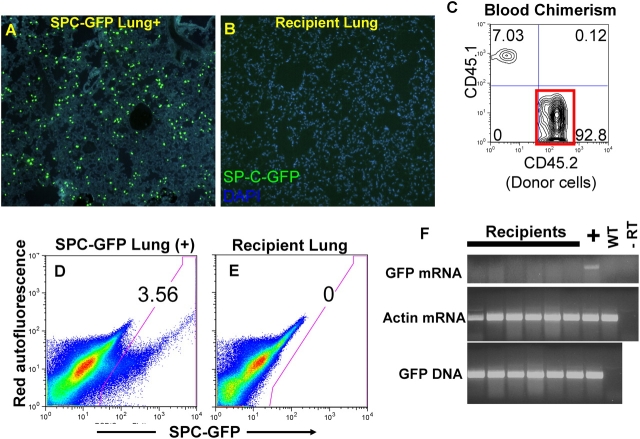
Figure 4.
Assessment of bone marrow–derived lung engraftment after transplantation of bone marrow cells from the SP-C–GFP lineage-specific reporter mouse. (A) Bright GFP fluorescence only in alveolar type II (AT2) cells is seen in lung frozen tissue sections from the transgenic (positive control) mouse. (B) Representative lung section from a recipient mouse 4 mo after transplantation of 10 million unfractionated bone marrow cells obtained from a donor SP-C–GFP mouse. No GFP+ engrafted cells are seen. (C) Peripheral blood analyzed from this same recipient shows 93% blood chimerism (red box) arising from the donor (CD45.2) transplanted marrow cells (recipient is a CD45.1 congenic mouse). (D) FACS analysis of 1 million live (propidium iodide excluding) lung cells from a SP-C–GFP transgenic mouse (positive control) shows GFP+ fluorescence in 3.56% of cells. (E) Representative FACS of 1 million live lung cells from a recipient transplanted with SP-C–GFP bone marrow shows no GFP+ events. (F) Representative analysis of RNA and DNA extracts from six recipients' lungs shows donor-derived cells are present in recipients' lungs (GFP DNA+), but are not AT2 cells because they do not express GFP mRNA. Controls are labeled as: “+” (SP-C-GFP transgenic lung); WT (wild-type lung); −RT (RNA extract from SP-C–GFP lung minus reverse transcription). RT-PCR of the housekeeping gene β-actin illustrates that cDNA is present in each sample.