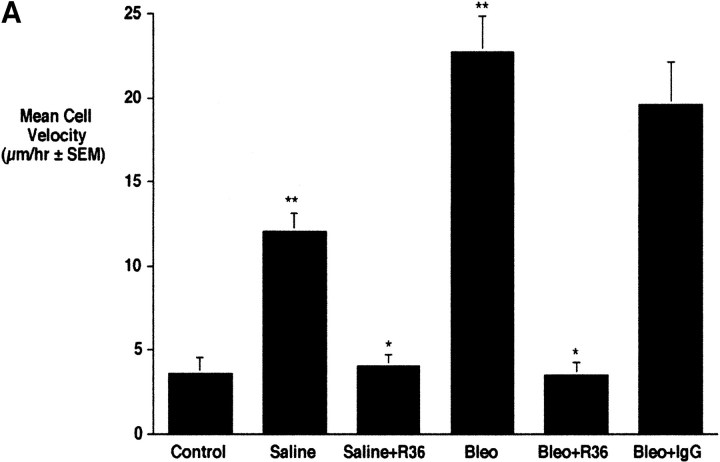
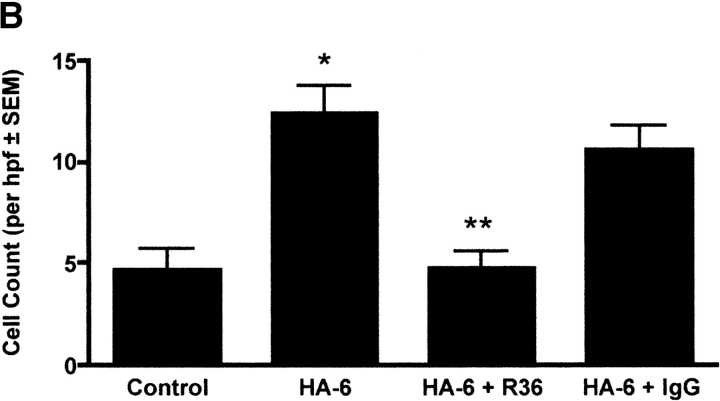
Figure 4.
Effect of anti-RHAMM antibody on macrophage motility 4 d after treatments. (a) Time-lapse cinemicrography was used to determine the effect of R36 on macrophage motility. Cells isolated from lavage of injured animals were plated and adherent macrophages were followed for 2 h after the addition of 5 μg/ml of R36. Nonimmune IgG was used as a control. Saline treatment alone caused some increase in macrophage motility. Bleomycin treatment resulted in a 5-fold increase in motility of macrophages. In both cases, motility was inhibited to baseline with R36 treatment, but not by nonimmune IgG. These data suggest that RHAMM fully accounts for increased macrophage motility after intratracheal treatment. (b) HA oligosaccharide-stimulated chemotaxis of RAW 264.7 cells was assessed using a modified Boyden chamber assay. HA-6 stimulated a 2.5-fold increase in macrophage chemotaxis that was completely blocked in the presence of R36, but not with normal rabbit IgG (P < 0.05, n = 6/condition, representative experiment of three repeats).