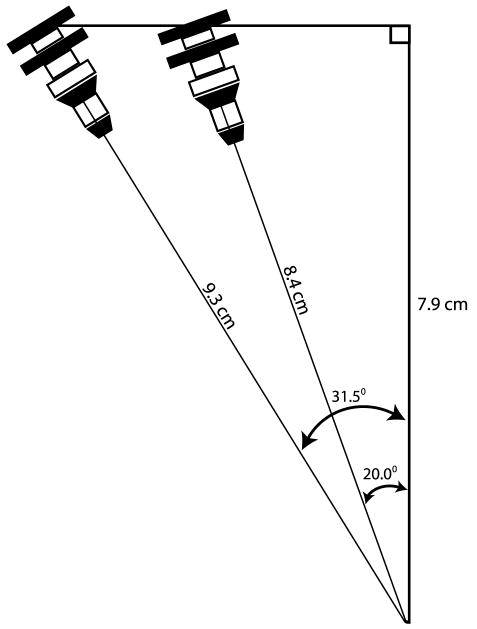
FIGURE 3.
The estimated transforaminal epidural depth using a lesser oblique angle would be close to the depth found in the present study. The median depth in the present study was 9.3 cm with an oblique angle of 31.5 degrees. The midline length, assuming a right-angled triangle, is 7.9 cm (cos A = adjacent length/hypotenuse). If a lesser oblique angle of 20 degrees is used, the estimated transforaminal epidural depth is 8.4 cm (9.7% less). A 10% difference is within the interquartile ranges shown in Table 2, thereby indicating that the epidural depth data reported in the present study are relevant regardless of the approach used.