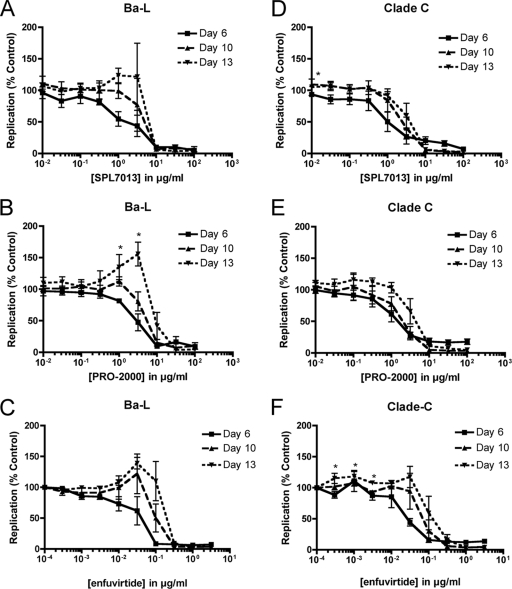
FIG. 1.
Inhibitory effects of SPL7013, PRO 2000, and enfuvirtide on the replication of HIVBa-L and the clade C 92BR025 strain in human PBMCs. PHA-stimulated PBMCs from at least one healthy donor were treated for 1 h with drug prior to infection with virus. Clarified culture supernatants collected at days 6, 10, and 13 postinfection were evaluated for virion-associated RT activity using a poly(rA)/oligo(dT) template/primer and [33P]dTTP as the substrate. Data are expressed as virus replication of drug-treated cultures compared to the infected untreated control (representing 100% replication). Data were obtained from at least three independent assays using PBMCs from different individuals for each assay, with data from four assays used for SPL7013 and PRO 2000 tested against both viruses with the exception of HIVBa-L on day 6 where data from three assays were used. For enfuvirtide, each data point represents data from three assays. The statistical significance of replication at greater than 100% of the infected, untreated control was determined using the nonparametric equality of medians Fisher's exact test where a P value of <0.05 was considered significant. As the alternative hypothesis was unidirectional (>100%), a one-sided test was applied. Drug concentrations with statistically significant increases in virus replication above the infected, untreated control are denoted with an asterisk. Error bars indicate the standard errors of the means.