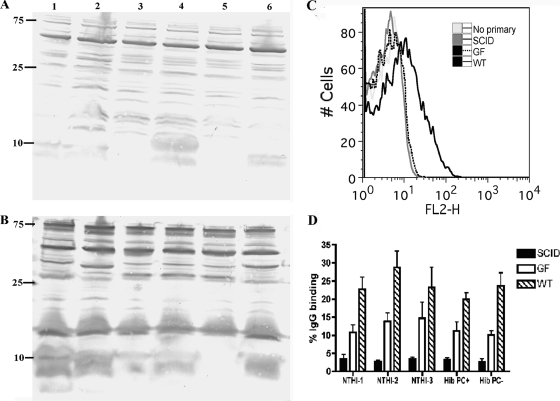
FIG. 5.
Natural antibody from conventionally reared mice recognizes targets expressed by all H. influenzae strains. (A and B) IgG antibodies from uninfected conventionally reared BALB/c mice recognize conserved H. influenzae targets by Western blot analysis. Whole-cell lysates of Hib with or without PC and without capsule (Cap−), NTHI-1, NTHI-2, and NTHI-3 were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membranes, and probed with sera from uninfected BALB/c mice (A) or immune sera (B) followed by alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-mouse IgG. Strains tested included NTHI-1 (lane 1), NTHI-2 (lane 2), Hib PC− (lane 3), Hib PC+ (lane 4), Hib Cap− (lane 5), and NTHI-3 (lane 6). Molecular mass markers are in kDa. (C and D) Natural antibodies from conventionally reared BALB/c mice bind to the surface of all H. influenzae strains tested. Flow cytometric analysis was conducted on each H. influenzae strain incubated with no serum (“No primary”) or uninfected sera from conventionally reared uninfected BALB/c mice (WT), GF uninfected mice (GF), or conventionally reared SCID mice (SCID) followed by phycoerythrin-labeled anti-mouse whole IgG. (C) Fluorescence intensity is represented on the x axis, and binding of the antibody to the surface of Hib (PC+) is indicated by a shift of the curve to the right. The image is representative of three independent experiments. Each serum source was added to reaction mixtures at a 1:20 dilution. (D) The percent IgG binding was determined by calculating the percentage of 10,000 events with an increase in mean fluorescence intensity compared to that of no-serum controls. Each H. influenzae strain was incubated with sera from WT (hatched bars), GF (open bars), or SCID (solid bars) BALB/c mice at a 1:100 dilution. Values are derived from three independent experiments and are shown ± standard deviations.