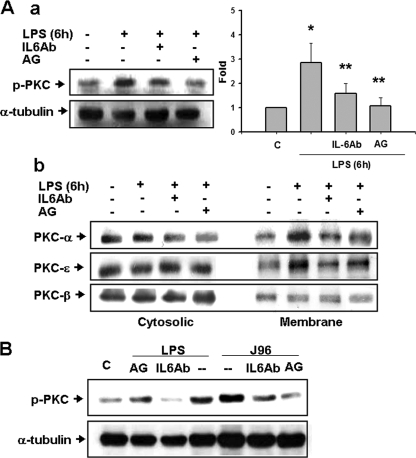
FIG. 6.
Activation of PKC in the urinary bladder of E. coli or endotoxin-treated mice. Urinary bladders were isolated from mice 6 h after intraperitoneal injection of E. coli endotoxin (LPS) (A) or 6 h after intravesical instillation of E. coli strain J96 (O4:K6) or LPS (B). In some experiments, mice were injected intraperitoneally (A) or instilled intravesically (B) with anti-IL-6 antibody (IL-6Ab) or aminoguanidine (AG, an iNOS inhibitor) at 30 min after E. coli treatment. PKC activation was assayed as the phosphorylation of PKC (Aa and B) and the translocation of PKC isoforms from cytosolic fraction to membrane fraction (Ab) by Western blot analysis using anti-phospho-PKC (pan) antibody and anti-PKC-α, -β, and -ɛ antibodies, respectively. α-Tubulin served as a control for sample loading and integrity. In Aa, the data are presented as means ± the SEM for six independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 compared to the control; **, P < 0.05 compared to LPS alone. In panels Ab and B, the results shown are representative of four independent experiments.