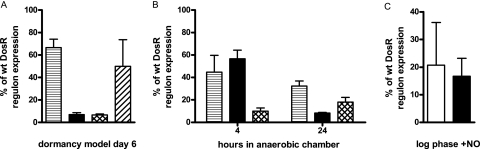
FIG. 1.
DosR regulon induction by DosT or DosS. Shown is the percent induction observed by microarray analysis of the DosR regulon genes of each mutant compared to those of the wild type (wt). (A) Anaerobic dormancy model sampled at day 6, 1 day after the onset of anaerobiosis. (B) Anaerobic GasPak chamber sampled at 4 and 24 h with single- and double-sensor mutants. Standard deviation is indicated. The ΔdosT mutant is horizontally striped, the ΔdosS mutant is black, the ΔdosS/T mutant is cross-hatched, and the ΔdosS/T mutant with constitutively plasmid-expressed dosT is diagonally striped. (C) Both DosT and DosS are able to respond to the NO stimulus provided by the NO donor diethylenetriamine/NO adduct via induction of the DosR regulon. The NO donor was added to log-phase cultures at a concentration of 0.1 mM, and they were incubated for 1 h. Shown is the percent induction observed by microarray analysis of the DosR regulon genes of each mutant compared to that of the wild type. Standard deviation is indicated. The white bar indicates data from the ΔdosT mutant strain, and the black bar indicates data from the ΔdosS mutant strain.