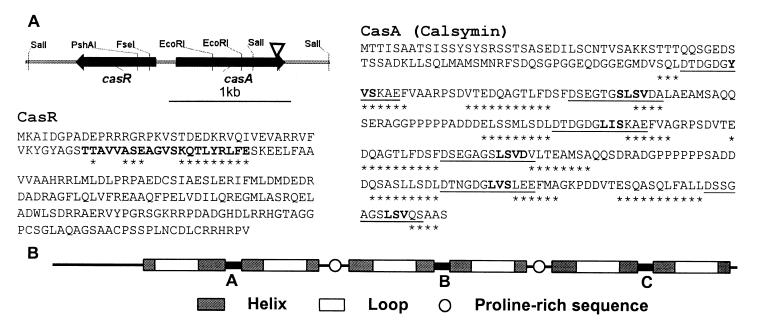
Figure 1.
Sequence and structure of the R. etli CasA (calsymin) and CasR proteins. (A) Schematic representation and physical map of the divergently transcribed casA and casR genes. The arrowhead indicates the position of the mTn5 insertion in the casA mutant FAJ1806. Predicted products of the casA and casR genes showing the six putative EF-hand calcium-binding sites of CasA and the helix–turn–helix structure of CasR. The secondary structure predictions are based on the algorithm of Geourjon and Deleage (28). Amino acids in boldface in the CasR sequence represent the conserved helix–turn–helix structure as found in TetR-related proteins (27). The amino acids in the CasR and CasA proteins marked with asterisks are part of predicted α-helices. Underlined amino acids in CasA are similar to EF-hand calcium-binding motifs (10). Amino acids forming putative short β-strands within the loops are in boldface. (B) Schematic representation of the three homologous calcium-binding domains of calsymin and localization of the EF-hand helix–loop–helix calcium-binding motifs and proline-rich domains.