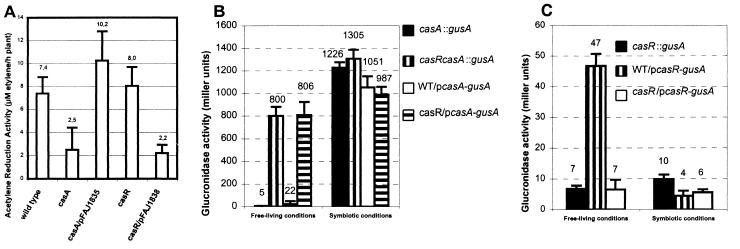
Figure 2.
Symbiotic phenotype of mutants and expression of R. etli casA and casR genes. (A) Nitrogen fixation of P. vulgaris plants inoculated with the R. etli wild-type strain, casA (FAJ1804) and casR (FAJ1802) mutant strains, and their complemented derivatives. Values are the mean ± SD (n = 10). The means are indicated above the bars. Plasmids pFAJ1835 and pFAJ1838 carry casA and casR genes, respectively. Similar results were obtained between strains FAJ1802 and FAJ1803 (casR mutants) and between strains FAJ1804 and FAJ1805 (casA mutants). (B and C) Expression of fusions between gusA and the casA (B) and casR (C) genes in free-living aerobic cultures (AMS) medium (13) supplemented with 10 mM sodium succinate, OD595 = 0.1–0.2, read with 100 μl culture in a Versamax microplate reader (Molecular Devices) and during symbiosis. Direct comparison of GusA activities under the two conditions may be difficult. Expressions were determined by using plasmid-borne PcasA–gusA (pFAJ1842) and PcasR–gusA (pFAJ1843) fusions and chromosomally located casA∷gusA (FAJ1806 and FAJ1807) and casR∷gusA (FAJ1809) fusions. β-Glucuronidase activities are expressed in Miller units. Values are the mean ± SD (n = 3).