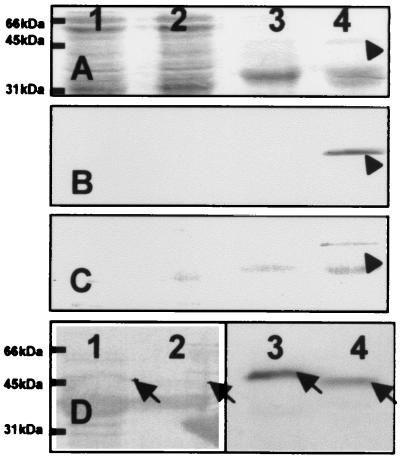
Figure 5.
Calcium binding and secretion of calsymin. (A–C) Staining of whole-cell proteins (lanes 1 and 2) and proteins secreted into the culture supernatant (lanes 3 and 4) from the R. etli wild-type CNPAF512 (lanes 1 and 3) and the casR mutant strain FAJ1803 (lanes 2 and 4). Proteins were subjected to electrophoresis on an SDS/polyacrylamide gel and transferred to PVDF membranes by electroblotting. The membranes were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (A) or incubated with 45Ca2+ and autoradiographed (B), or the calcium-binding proteins were stained with ruthenium red (C). The protein band indicated with an arrow was identified as calsymin by N-terminal sequence analysis of the isolated protein. (D) Calcium binding and secretion of a truncated calsymin protein from R. etli cultures. Proteins were isolated from the culture supernatant of R. etli FAJ1803 (lanes 1 and 3) and strain casA∷mTn5gusA-pgfp21 casR∷Ω-Spc FAJ1808 (lanes 2 and 4). The membrane was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (lanes 1 and 2) or incubated with 45Ca2+ and autoradiographed (lanes 3 and 4). The wild-type (lanes 1 and 3) and truncated (lanes 2 and 4) calsymin proteins are marked with an arrow.