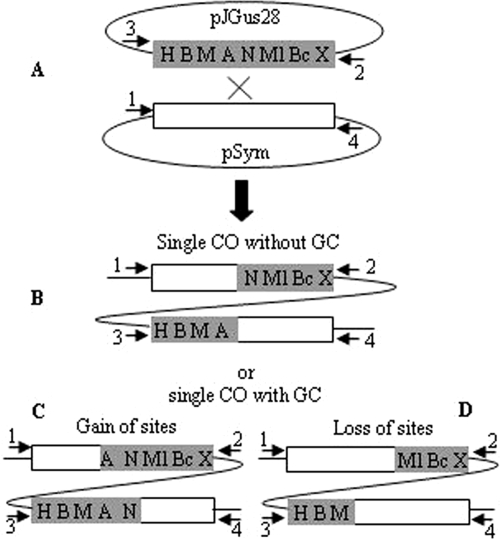
FIG. 2.
Experimental strategy for analyzing gene conversion. (A) The modified nifH gene is represented by a gray rectangle, and capital letters indicate different restriction sites as follows: H, HindIII; B, BamHI; M, MaeIII; A, ApaLI; N, NarI; Ml, MluI; Bc, BclI; X, XbaI. The only wild-type nifH gene of the symbiotic plasmid of R. etli is depicted as a white rectangle. Upon recombination of pJGus28 and pSym (a cross between both nifH genes), we could expect a reciprocal recombination event (markers are just redistributed) (B), a nonreciprocal recombination event to a gain of sites (note the central markers A and N) (C), or a loss of sites (note that the central markers A and N have been lost in both parts of the cointegrate) (D). Arrows in all panels represent the specific primers used for amplifying each nifH gene in the cointegrate molecule.