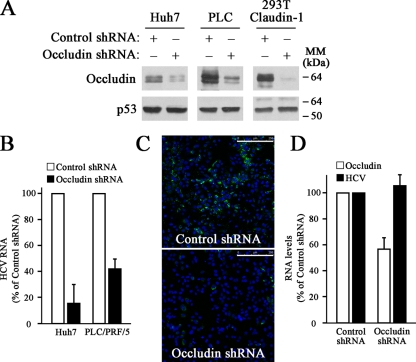
FIG. 1.
HCVcc infection is impaired by occludin knockdown. (A) Occludin was silenced using shRNA technology on Huh7, PLC/PRF/5 (PLC), and 293T-Claudin-1 cells. Occludin knockdown was confirmed by Western blotting using antioccludin and anti-p53 (loading control) antibodies. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated to the right of the blots. Results are representative of two independent experiments. (B) Cells were infected with HCVcc, and 1-μg RNA samples were analyzed by real-time RT-PCR using specific primers to determine HCV RNA levels. Histone H3 mRNA levels were used for sample normalization. Data are expressed as HCV RNA levels relative to control shRNA-transduced cells. Data are represented as the mean values plus standard deviations (SD) (error bars) from three experiments. (C) HCVcc-infected Huh7 cells were processed for immunostaining using an antibody directed specifically against HCV core protein (green). The merged image with the nuclei stained with 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue) is shown. Results are representative of two separate experiments. Bars, 250 μm. (D) Occludin was silenced using shRNA technology on Huh7 clones harboring the genomic replicon I389/Core-3′/5.1 (HCV-G1) or the subgenomic replicon I377/NS3-3′ (HCV-NSA). Occludin and HCV RNA levels were determined by real-time RT-PCR as described in Materials and Methods. Data are expressed as the mean values plus SD (error bars) of the results obtained with both clones.