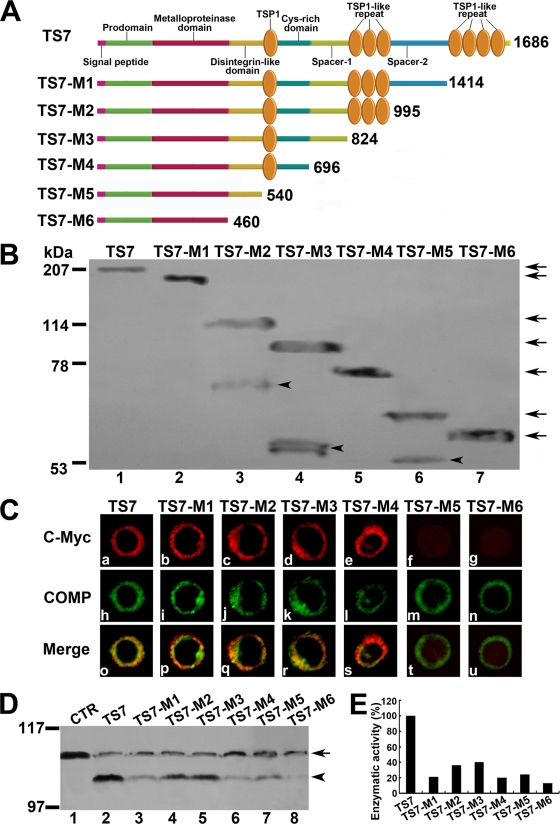
FIG. 5.
Effects of ADAMTS-7 functional domains on its cell surface location and enzymatic activity. (A) Schematic structure of the ADAMTS-7 and its C-terminal deletion mutants. Numbers refer to amino acid residues in ADAMTS-7. The functional domains are indicated. (B) Western blotting analysis of ADAMTS-7 and its C-terminal deletion mutants. The conditioned medium collected from HEK 293-ENBA cells stably transfected by either ADAMTS-7 or its C-terminal deletion mutants was detected by Western blotting analysis with anti-c-Myc antibodies. The arrows indicate the full length of the ADAMTS-7 and its series of mutants, and the arrowheads indicate the fragments resulted from several ADAMTS-7 deletion mutants. (C) The subcellular localization of the ADAMTS-7 and its domain deletion mutants in RCS cells. RCS chondrocytes were transiently transfected with expression constructs encoding the ADAMTS-7 and its C-terminal deletion mutants. The expression of ADAMTS-7 or its C-terminal deletion mutants was visualized with anti-c-Myc antibodies. COMP was visualized by cell staining with polyclonal anti-COMP antibodies. Overlapping signals are indicated with “Merge.” (D) In vitro digestion assays of COMP mediated by ADAMTS-7 and its C-terminal domain deletion mutants. Purified COMP (200 nM) was incubated with the conditioned medium collected from HEK 293-EBNA cells stably transfected by pcDNA3.1 (CTR), ADAMTS-7 (TS7), or its C-terminal domain deletion mutants (TS7-M1 to TS7-M6), as indicated. The cleaved products were subjected to reduced 8% SDS-PAGE and detected with polyclonal anti-COMP antibodies. The intact COMP and its digested fragments are indicated with an arrow and arrowhead, respectively. (E) Qualitative analysis of enzymatic activity of ADAMTS-7 and its C-terminal domain deletion mutants. The values were calibrated against ADAMTS-7 (TS7), here given the value of 100%.