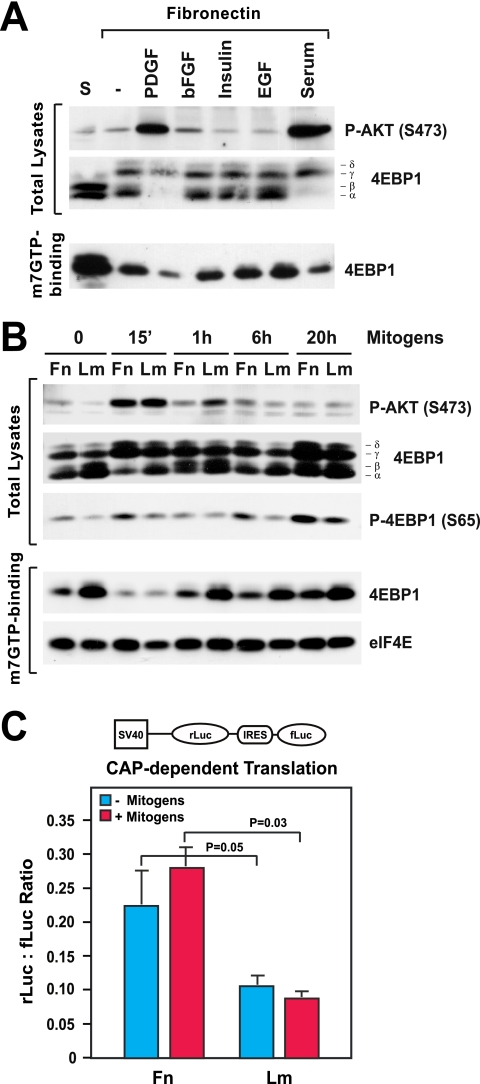
FIG. 1.
Integrin-specific adhesion promotes mTORC1 signaling and cap-dependent mRNA translation. (A) Matrix adhesion promotes phosphorylation of 4EBP1 without causing significant activation of AKT. MEFs were detached and kept in suspension (S) or plated onto fibronectin in the presence of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF; 10 ng/ml), bFGF (20 ng/ml) along with 1 μg/ml heparin, insulin (10 ng/ml), EGF (10 ng/ml), or fetal calf serum (10%) for 6 h. Equal amounts of total proteins or proteins binding to m7GTP-Sepharose were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies to the indicated antigens. −, control with no serum or growth factor; P-AKT (S473), AKT phosphorylated at S473. (B) Integrin-specific signaling sustains the activation of mTORC1 during the G1 phase. HUVECs were plated onto fibronectin (Fn) or laminin 1 (Lm) in the presence mitogens (20 ng/ml bFGF, 1 μg/ml heparin, 10 ng/ml insulin, 10 μg/ml transferrin, and 10 ng/ml EGF) for the indicated times. Equal amounts of total proteins or proteins binding to m7GTP-Sepharose were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies to the indicated antigens. 15′, 15 min; P-4EBP1 (S65), 4EBP1 phosphorylated at S65. (C) HUVECs were transfected with the bicistronic reporter construct depicted above the graph, deprived of serum, and plated onto either fibronectin or laminin 1 in the absence (−) or presence (+) of mitogens for 24 h. The graph shows the mean ratios ± standard deviations (SD) between Renilla luciferase (rLuc) and firefly luciferase (fLuc) bioluminescence levels in the indicated samples. SV40, simian virus 40; IRES, internal ribosome entry site.