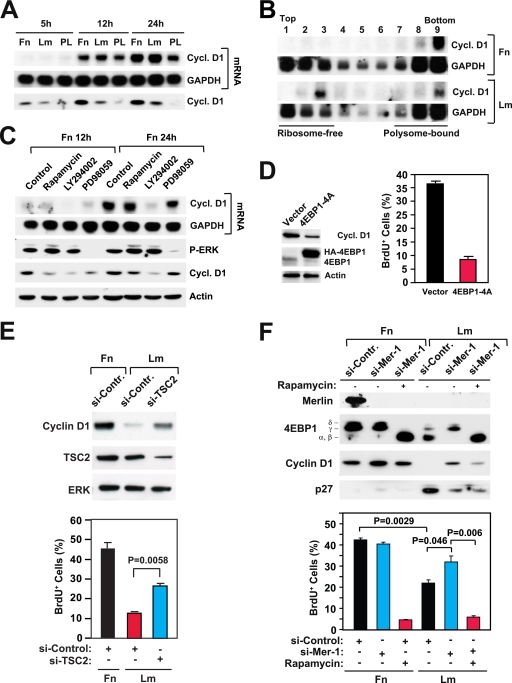
FIG. 4.
Integrin-specific mTORC1 signaling controls the translation of cyclin D1 mRNA and promotes cell cycle progression. (A) Integrin-specific signaling is not required for the transcription of cyclin D1. HUVECs were plated onto fibronectin (Fn), laminin 1 (Lm), or the control substrate poly-l-lysine (PL) in the presence of mitogens. Northern blotting was used to examine the levels of mRNAs encoding cyclin D1 (cycl. D1) and GAPDH at the indicated time points. (B) Integrin-specific signaling promotes association of the mRNA encoding cyclin D1 with polysomes. Samples of total mRNA from HUVECs plated onto fibronectin or laminin 1 for 16 h in the presence of growth factors (20 ng/ml bFGF, 1 μg/ml heparin, 10 ng/ml insulin, 10 μg/ml transferrin, and 10 ng/ml EGF) were fractionated on sucrose density gradients. Northern blotting was used to examine the levels of mRNAs encoding cyclin D1 and GAPDH in each gradient fraction. (C) Rapamycin inhibits translation of the mRNA encoding cyclin D1. HUVECs synchronized in G0 were detached and plated onto fibronectin in the presence of growth factors without or with 5 nM rapamycin, 20 μM LY294002, or 40 μM PD98059. At the indicated time points, cells were lysed and subjected to either Northern analysis with the indicated probes (upper two panels) or immunoblotting with antibodies to the indicated antigens (lower two panels). P-ERK, phosphorylated ERK. (D) Disruption of cap-dependent translation inhibits induction of cyclin D1 and cell cycle progression. HUVECs were transfected with an empty vector or a vector encoding a hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged form of the phosphorylation-defective mutant 4EBP1-4A. After 48 h, cells were synchronized in G0, detached, and plated onto fibronectin in the presence of mitogens and BrdU for 24 h. (Left) Total cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies to the indicated antigens. (Right) The graph shows the percentages of cells entering S phase under the indicated conditions. The experiment was done three times. (E) Depletion of TSC2 partially rescues expression of cyclin D1 and progression through the cell cycle on laminin 1. HUVECs were transfected with the indicated siRNAs, synchronized in G0, and plated onto fibronectin or laminin 1 for 24 h. (Top) Total lysates were subjected to immunoblotting using antibodies to the indicated antigens. (Bottom) Cells were subjected to BrdU incorporation and anti-BrdU staining. The graph illustrates the mean percentages ± SD of BrdU-positive (BrdU+) cells. si-Contr., control siRNA; si-TSC2, siRNA targeting TSC2; +, present; −, absent. (F, top) Depletion of merlin partially rescues expression of cyclin D1 on laminin 1 through a rapamycin-sensitive pathway. HUVECs were transfected with the indicated siRNAs, synchronized in G0, and then plated onto fibronectin or laminin 1 in the presence of growth factors for 24 h without (−) or with (+) 5 nM rapamycin. Equal amounts of total proteins were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies to the indicated antigens. (Bottom) Depletion of merlin partially rescues progression through G1 on laminin 1 through a rapamycin-sensitive pathway. HUVECs were transfected with a control siRNA (si-Contr., or si-Control) or an siRNA targeting merlin (si-Mer-1), synchronized in G0, and plated onto fibronectin or laminin 1 in the presence of growth factors and BrdU for 24 h without or with 5 nM rapamycin. The graph shows the mean percentages ± SD of BrdU+ cells under the indicated conditions.