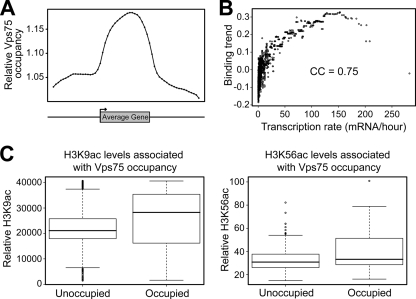
FIG. 3.
Genome-wide analysis of Vps75 binding sites reveals an association with transcription and histone acetylation. (A) Composite profile of Vps75 occupancy (detected by ChIP) across the average gene. The ends of genes were defined at fixed points according to the positions of transcriptional start and termination sites. The gene and the flanking (upstream and downstream) regions were then subdivided into 20 regions each. For each of the 60 intervals, a mean Vps75 occupancy was calculated and plotted. (B) Vps75 occupancy correlates with the transcription rate genome-wide. The Vps75 binding trend was determined as described previously (44) and plotted against the transcription rate for all yeast genes (20). The Pearson CC is shown. (C) H3K9ac and H3K56ac levels are higher at sites of Vps75 occupancy. Box plots show histone H3K9 (left) and H3K56 (right) acetylation levels at Vps75-occupied and -unoccupied regions, generated by comparing peaks of Vps75 occupancy with published maps of histone acetylation (26, 50). The line in the center of each box represents the median value of the distribution, and the upper and lower ends of the box are the upper (25th) and lower (75th) quartiles, respectively.