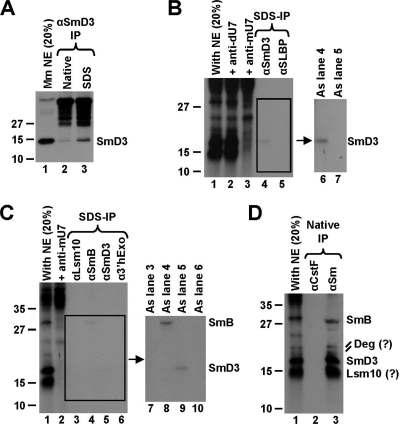
FIG. 5.
Identification of U7-dependent cross-links. (A) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of SmD3 from a mouse nuclear extract by a specific anti-SmD3 mouse monoclonal antibody under native (lane 2) or denaturing (lane 3) conditions. Lane 1 contains 20% of the extract used for each immunoprecipitation. (B) Immunoprecipitation of cross-linked proteins by the anti-SmD3 antibody. A processing reaction mixture containing the 5′-labeled DCPmax/s substrate was UV irradiated, treated with RNase T1, denatured by boiling in the presence of SDS, and incubated with the anti-SmD3 (lanes 4 and 6) or anti-SLBP (lanes 5 and 7) antibody. Precipitated proteins were resolved in an SDS-polyacrylamide gel and detected by autoradiography. The input (20%) is shown in lane 1. An image of the boxed gel fragment observed after a longer exposure time (lanes 4 and 5) is shown to the right. Cross-links formed in the presence of the anti-dU7 and the anti-mU7 oligonucleotides are shown in lanes 2 and 3, respectively. (C) Immunoprecipitation of cross-linked proteins by antibodies indicated at the top of each lane. The experiment was carried out as described for panel B. The input (20%) is shown in lane 1. An image of the boxed gel fragment observed after a longer exposure time (lanes 3 to 6) is shown to the right. Cross-links formed in the presence of the anti-mU7 oligonucleotide are shown in lane 2. (D) Immunoprecipitation of cross-linked proteins by the anti-Sm Y12 monoclonal antibody under native conditions. A monoclonal antibody against CstF-77 was used as a negative control (lane 2). The input (20%) is shown in lane 1.