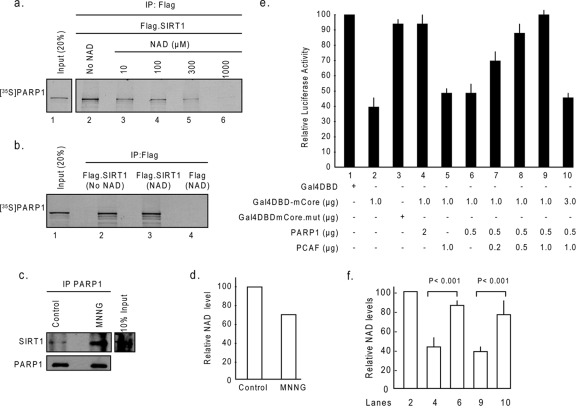
FIG. 5.
NAD levels dictate PARP1-SIRT1 interaction. (a) Beads containing Flag-SIRT1 were incubated with [35S]methionine-labeled PARP1 ([35S]PARP1) in a protein binding buffer containing either no NAD or gradually increasing concentrations of NAD. Beads were then separated and washed, and proteins bound to beads were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and then by autoradiography. (b) Flag-SIRT1 or Flag alone (negative control) was incubated with NAD (1 mM) in separate tubes. The NAD-bound Flag-SIRT1 or Flag was then incubated with [35S]methionine-labeled PARP1 not bound to NAD. Beads were separated, and coprecipitation of [35S]methionine-labeled PARP1 with Flag beads was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and then by autoradiography. (c) HeLa cells were treated with 100 μM of MNNG for 15 min. PARP1 was immunoprecipitated from the lysate, and the resulting beads were analyzed by Western analysis with anti-SIRT1 and anti-PARP1 antibodies. (d) Relative NAD levels in the same cell lysate (n = 4). (e) PARP1 and SIRT1 counteract each other's activity. Cos7 cells were cotransfected with the reporter plasmid (0.5 μg) and different combinations of expression plasmids (described in Materials and Methods) as shown below each bar diagram. Forty-eight hours following transfection, cells were harvested, and the luciferase activity was measured. The expression of β-Gal was used as a reference control. Values are means ± the standard errors (SE) of the results for five experiments. (f) NAD content levels in selected transfectants (n = 5). +, present; −, absent.