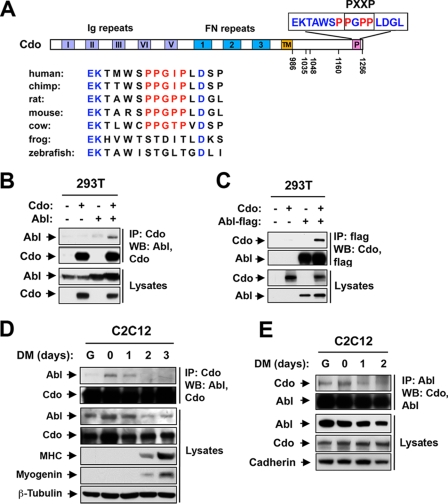
FIG. 1.
Cdo interacts with Abl. (A) Schematic of the Cdo intracellular region, highlighting the PXXP motif and surrounding sequences from several species. Numbering is from rat Cdo, from which expression constructs are derived. Note that the frog (Xenopus laevis) and zebrafish (Danio rerio) Cdo sequences lack this motif, despite conserved amino acids that flank the motif. Chicken (Gallus gallus) Cdo lacks a region that clearly aligns with these sequences (not shown). TM, transmembrane. (B) Lysates of 293T cells transiently transfected with Cdo, Abl, or control (−) expression vectors, as indicated, were immunoprecipitated (IP) with an antibody to Cdo and then Western blotted (WB) with Cdo or Abl antibodies. Note that Cdo is not expressed endogenously in 293T cells (22). (C) Lysates of 293T cells transiently transfected with Cdo, Flag-tagged Abl, or control (−) expression vectors, as indicated, were immunoprecipitated with an antibody to the Flag epitope and then Western blotted with Cdo or flag antibodies. (D) Lysates of C2C12 cells that were proliferating in GM (lane G), at near confluence (0) or in DM for the indicated times were immunoprecipitated with antibodies to Cdo and Western blotted with Abl or Cdo antibodies. Straight lysates were also Western blotted with antibodies to Abl and Cdo, to myogenin and MHC to monitor differentiation, and to β-tubulin as a loading control. (E) Same as in panel D, except that lysates were immunoprecipitated with antibodies to Abl and Western blotted with Abl or Cdo antibodies, and straight lysates were blotted with antibodies to Abl and Cdo and to pan-cadherin as a loading control.