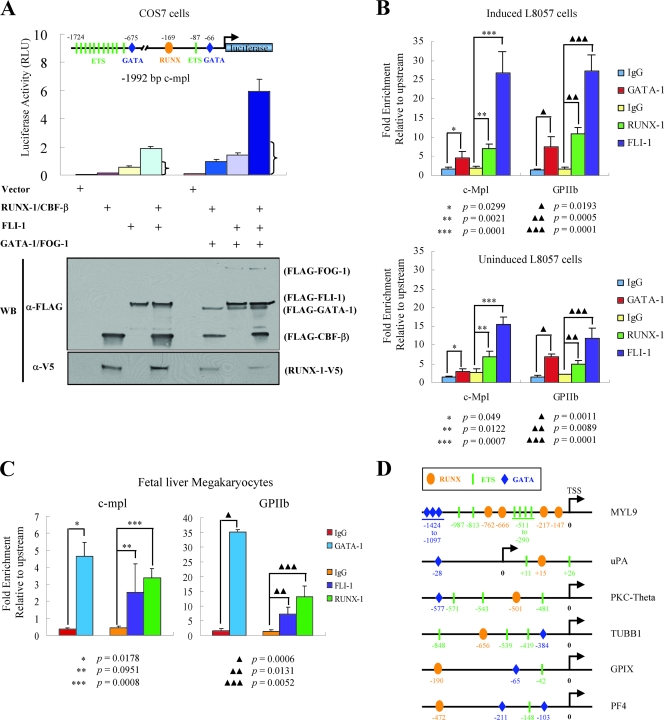
FIG. 4.
Functional synergy between FLI-1 and RUNX-1. (A) Transcriptional reporter assays of the c-mpl promoter. A reporter construct consisting of 1,992 bp of the murine c-mpl promoter linked to the firefly luciferase cDNA was cotransfected with an empty expression plasmid or plasmids expressing RUNX-1-V5 and/or FLAG-CBF-β, FLAG-FLI-1, FLAG-GATA-1, and FLAG-FOG-1, as indicated. The positions of the RUNX, ETS, and GATA binding motifs relative to the natural transcriptional start site are indicated in the diagram of the reporter construct. RUNX, oval; ETS, rectangle; GATA, diamond. Luciferase activity was measured after 48 h and is indicated on the y axis. The mean ± standard error of the mean from three independent transfections is indicated. The bracket indicates the expected level if RUNX-1/CBF-β and FLI-1 acted additively (sum of the activation of RUNX-1/CBF-β and FLI-1 alone). Western blot (WB) analysis showing expression levels of the various proteins (10% of whole-cell lysate) from one representative experiment is displayed at the bottom. RLU, relative light units; α-, anti-. (B) Quantitative ChIP assays showing occupancy of the c-mpl and GPIIb promoters by GATA-1, RUNX-1, and FLI-1 in induced (TPA, 50 nM, for 72 h) (top) and uninduced (bottom) L8057 cells. The levels of enrichment at the c-mpl and GPIIb promoters using anti-GATA-1, anti-RUNX-1, or anti-FLI-1 antibodies or control rat (for GATA-1) or rabbit (for RUNX-1 and FLI-1) IgG are shown relative to a negative control region located −7.5 kb upstream of the c-mpl promoter transcriptional start site. Results represent the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. (C) Quantitative ChIP assay for GATA-1, RUNX-1, and FLI-1 occupancy of the c-mpl and GPIIb promoters in mature primary fetal liver-derived megakaryocytes and as described in panel B. The results show the mean from three independent experiments for RUNX-1 and FLI-1 and two independent experiments for GATA-1, ± standard deviation. (D) Schematic diagram showing the presence of putative RUNX, ETS, and GATA factor binding motifs in the promoters of the genes for human MYL9, uPA, PKC-theta, β1-tubulin (TUBB1), GPIX, and rat PF4.