FIG. 6.
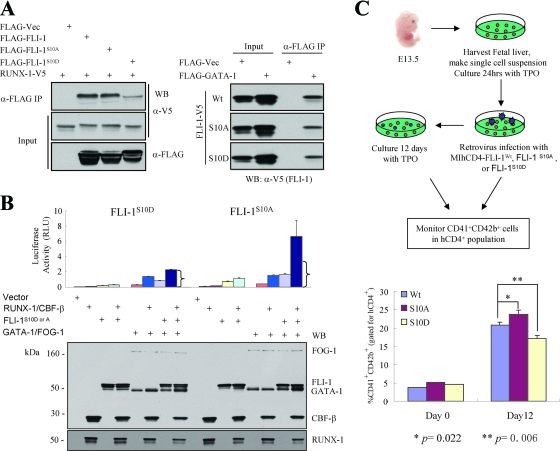
Requirement of FLI-1 Ser10 dephosphorylation for efficient RUNX-1-FLI-1 interaction and megakaryocytic differentiation. (A) FLI-1 S10D mutation disrupts RUNX-1-FLI-1 interaction (left) but does not interfere with FLI-1-GATA-1 interaction (right). (Left) The empty FLAG vector or FLAG-tagged wild-type FLI-1, FLI-1S10A, or FLI-1S10D mutants were coexpressed with RUNX-1-V5 in COS-7 cells, as indicated. (Right) The empty FLAG vector or FLAG-tagged GATA-1 was cotransfected with V5-tagged wild-type FLI-1, FLI-1S10A, or FLI-1S10D mutants, as indicated. In both experiments, immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed using an anti-FLAG antibody from crude nuclear extracts, and copurified material was analyzed by Western blotting, using anti-V5-HRP or anti-FLAG-HRP. A 2.5% input is shown. Representative Western blots are shown. See Fig. S3 in the supplemental material for repeat co-IP experiments and co-IP in the reverse direction. Vec, vector; α-, anti-. (B) Loss of FLI-1/RUNX-1 synergistic c-mpl activation by FLI-1S10D substitution. Transcriptional reporter assays were performed as described in the legend to Fig. 4, except FLAG-FLI-1S10A and FLAG-FLI-1S10D were substituted for FLAG-tagged wild-type FLI-1. Brackets indicate the expected activity level if RUNX-1/CBF-β and the FLI-1 mutants were acting additively only. The bottom panel shows Western blot analysis of all the expressed proteins; 10% input of whole-cell lysis is shown. RLU, relative light units. (C) Dominant-negative effect of FLI-1S10D on differentiation of primary megakaryocytes. (Top) Schematic diagram showing experimental design. (Bottom) Percentage of CD41+/CD42b+ double-positive cells (after gating for human CD4+ population) immediately after the 2-day retroviral infection (day 0) or 12 days after retroviral infection. Results represent the mean ± standard error of the mean from three independent experiments. P values (Student's t test) were calculated relative to the wild-type overexpression sample. Wt, wild type.