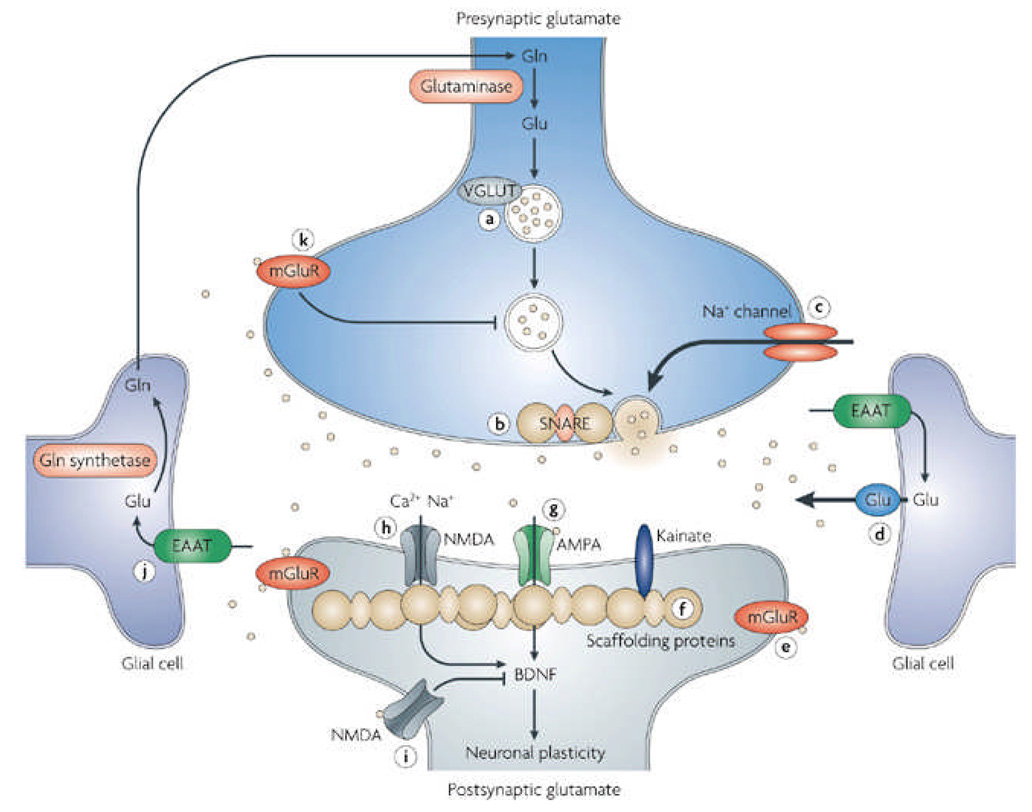
Figure 1. Glutamatergic neurotransmission and potential targets for drug development.
Tight physiological control is maintained over glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamine (Gln) is converted to glutamate (Glu) by glutaminase, though it can also be derived from the TCA cycle (not shown). Glu is packaged into presynaptic vesicles by the vesicular Glu transporter (VGLUT) proteins and released from the neuron in an activity-dependent manner through interactions with SNARE proteins. Glu is cleared from the extracellular space by excitatory amino acid transporters (EAATs) present predominantly on glia. In glial cells Glu is converted to Gln by Gln synthetase (GS). A variety of Glu receptors are present on presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons as well as on glial cells. These include both ionotropic receptors (AMPA, NMDA, and KA), as well as metabotropic receptors (mGluRs). The effect of Glu is determined by the receptor subtype, localization, and interactions with various scaffolding and signaling proteins in the postynaptic density (PSD). Activation of Glu receptors results not only in rapid ionotropic effects, but also in long-term synaptic plasticity.
Potential Targets for Drug Development numbered in the figure:
1) AMPA receptor modulation; 2) NMDA receptor modulation (a) extrasynaptic, (b) synaptic; 3) Group I metabotropic receptor modulation; 4) Voltage dependent Na+ channel modulation that regulates Glu release; 5) Group II metabotropic receptor modulation (mGluR2/3 receptor antagonists have demonstrated antidepressant activity, mGluR2/3 agonists have demonstrated axiolytic activity); 6) Facilitation of Glu clearance by EAATs; 7) Modulation of extrasynaptic Glu release. 8) PSD proteins. Theoretically, it is possible that agents capable of modifying the expression or function of PSD proteins could be used to treat mood disorders; 9) Modulation of presynaptic vesicular Glu release; 10) Modulation of presynaptic vesicular loading of Glu.
Gln=glutamine; Glu=glutamate; VGLUT=vesicular glutamate transporter; mGlu metabotropic glutamate transporter; EAAT=excitatory amino acid transporter; Ca=calcium; Na=sodium; NMDA=N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; AMPA= α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-isoxazole-4-propionic acid receptor; BDNF=brain derived neurotrophic factor; TCA=tricarboxylic acid cycle; Ac-CoA=acetyl-CoA; α-KG= α-ketoglutarate; SNARE=soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor attachment receptor complex.