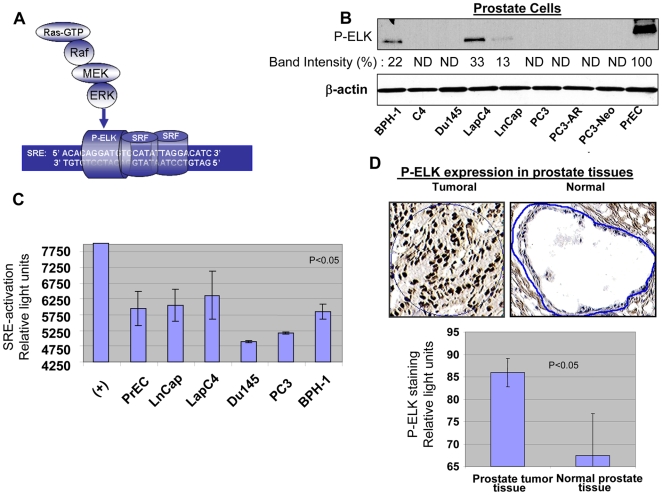
Figure 2. Ras signaling and activation of ERK/ELK/SRE in prostate cells and tissue.
Activation of Ras leads to initiation of a signal via Raf/MEK/ERK which in turn phosphorylates/activates transcription factor ELK. ELK in combination with SRF drives expression from promoters containing SRE elements. (A) Activation of ERK and phosphorylation of ELK in a series of prostate cells including prostate cancer cells, PrECs and BPH-1 is evaluated by in-vitro kinase assay for P-ERK. Band intensities are evaluated in comparison to the strongest band which in this case was the band for PrEC represented as 100%, ND stands for not detectable. (B) Activation of SRE by binding of P-ELK was evaluated by performing a Luminex-based assay. Existence of P-ELK and its binding to SRE elements protects these oligomers from digestion by a nuclease and allows generation of light. (C) Expression of P-ELK (active ELK) in malignant prostate tissue samples (n = 10, average Gleason score 6.0) and non-malignant prostate tissue was evaluated by performing immunohistochemistry and following image analysis for dark brown nuclear staining representing P-ELK using appropriate software. Upper panels show a sample of P-ELK staining for tumoral and normal tissues while the lower panels show average of staining intensity for P-ELK in different samples.