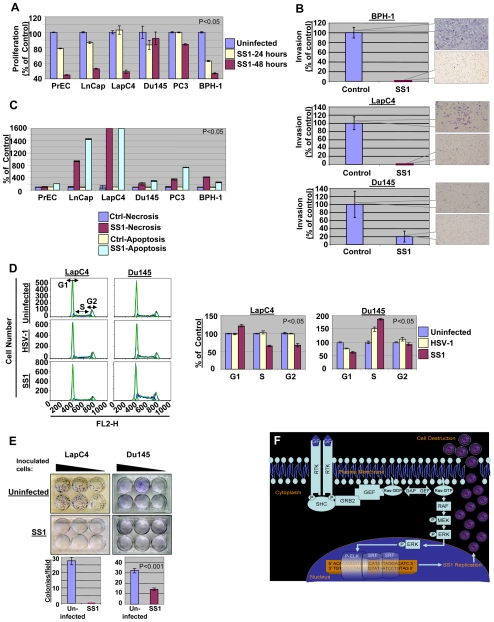
Figure 4. The effects of SS1 infection on the phenotype of prostate cells.
The proliferation rate of prostate cells is decreased upon exposure to SS1 virus (MOI∼1) with lower levels observed in case of prostate cancer cells with high Ras signaling (LnCap and LapC4) and PrEC and BPH-1 cells as compared to Du145 and PC3 cells (low Ras cells). (A) Invasiveness of prostate cancer cells LapC4 and Du145 as well as BPH-1 cells were decreased after 24 hours of exposure to SS1 virus in a significant manner. The decrease in invasiveness was more prominent for cells with elevated Ras signaling (LapC4 and BPH-1) as compared with Du145. Control Du145 cells were much less invasive than other cells. (B) Increase in necrosis and apoptosis is observed upon exposure of prostate cells to SS1 virus. The induction in necrosis/apoptosis is remarkably greater in LnCap and LapC4 cells. (C) The progression of cell cycle is altered upon exposure of prostate cancer cells to SS1 virus. In case of a high Ras cell (LapC4) an increase in G1 and decrease in S and G2 was observed upon infection with SS1 as compared with parental virus infected and control cells. Du145 (a low Ras cell), however, showed a passage through G1 but significant enhancement of S1 fraction. Left panels represent captured data plotted as fluorescence intensity (FL2-H channel) versus cell number for different phases of cell cycle. The right panel portrays these data as percentage of control (non-infected cells) for SS1 or HSV-1 infected cells. (D) Colony formation capability of LapC4 and Du145 cells was also significantly reduced upon infection with SS1. Upper panels show formation of colonies for a range of number of inoculated infected cells. The lower panels show average number of colonies per microscopy field for SS1-infected and control groups. The colony forming capability of Du145 cells were less inhibited as compared to LapC4 cells. (E) The mechanism of SS1 action is illustrated in this figure. Activation of Ras signaling pathway stimulates a signal through Raf/MEK/ERK pathway inducing phosphorylation of ELK. Stimulation of SRE elements by a complex including P-ELK results in expression of ICP4 and replication of SS1 which eventually destroys the cell via infection.