Fig. 2.
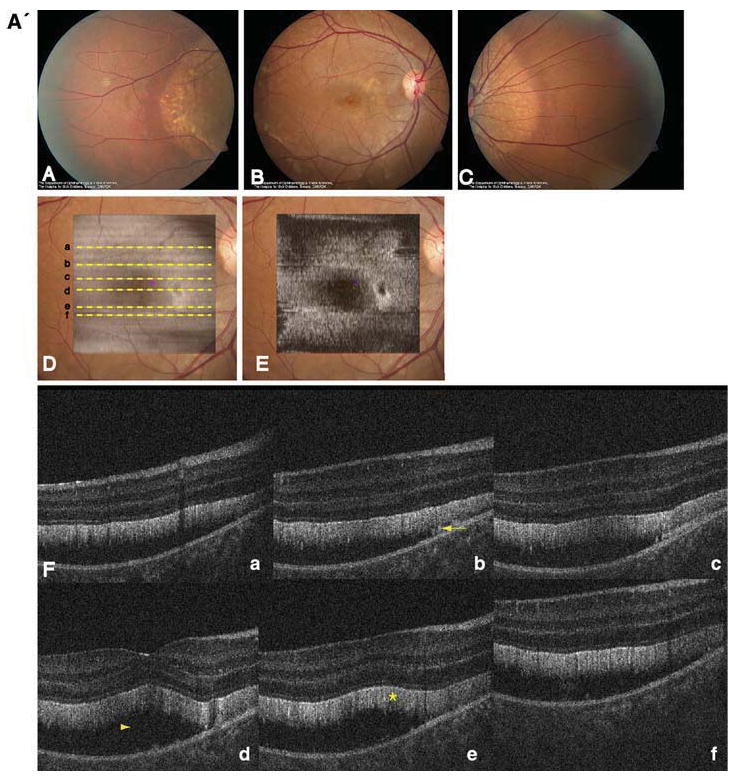
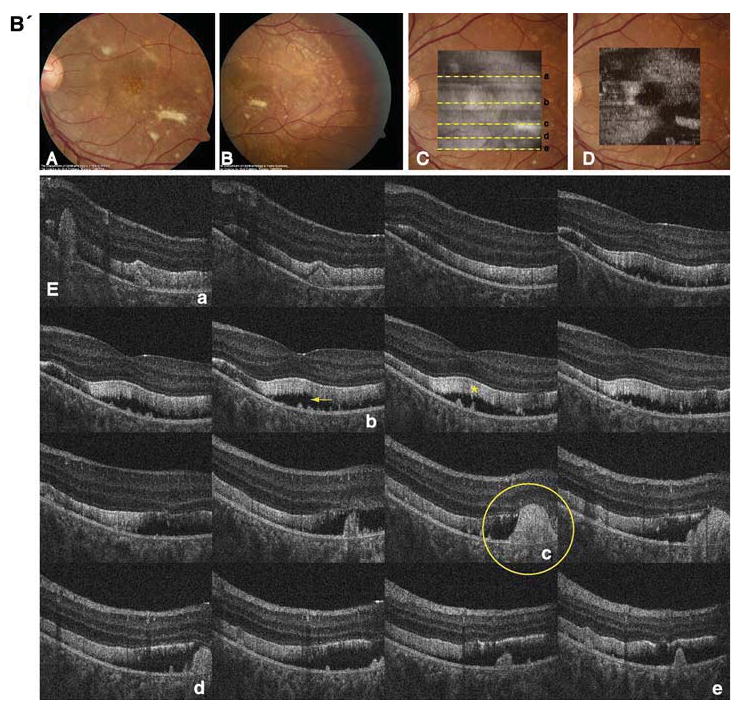
A' Composite of color fundus photographs and serial horizontal Fd-OCT scans (6 mm) of the right eye. Fundus photograph shows a well-demarcated area with round yellowish-white deposits at the posterior pole (A) extending to the temporal (B) and nasal (C) periphery. The locations of OCT B-scans are denoted by lines (a–f) shown on the OCT fundus image (intensity projection of the OCT volume), which is superposed and registered to the color fundus photo. (D) Virtual C-scan at the level of the photoreceptor inner/outer segment junction segmented from the reconstructed OCT volume is shown. (E) B-scans (F) illustrate deposits (denoted by an arrow in one scan) within the RPE with RPE detachment from the photoreceptors (arrowhead in one scan). Photoreceptor outer segments are thickened and elongated (indicated by a star in one scan). B' Composite of color fundus photograph and serial horizontal Fd-OCT scans (6 mm) of the left eye. Fundus photograph shows a well-demarcated area with round yellowish-white deposits at the posterior pole (A) extending to the temporal (B) and nasal (not shown) periphery. Subretinal fibrosis is visible inferior-temporal and superior-nasal of the fovea. The locations of OCT B-scans are denoted by lines (examples a–e) shown on the OCT fundus image, which is superposed and registered to the color fundus photo. (C) Virtual C-scan at the level of the photoreceptor inner/outer segment junction segmented from the reconstructed OCT volume is shown. (D) B-scans (E) demonstrate RPE detachment from the photoreceptors. Photoreceptor outer segments are thickened and elongated (indicated by a star in one scan). Small bridges between the photoreceptor outer segments and RPE are visible as denoted by an arrow in the scan through the fovea (b). Circle illustrates extensive RPE deposits extending to the outer plexiform layer
