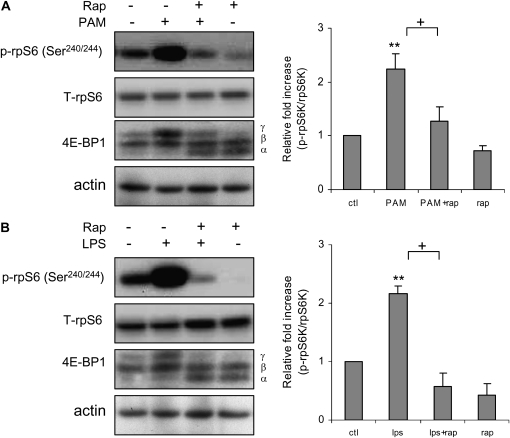
Figure 2.
Rapamycin inhibits PAM- or LPS-induced mTORC1 activation. Bone marrow neutrophils were cultured with rapamycin (0 or 30 nM) for 30 minutes, followed by addition of PAM (0 or 1 μg/ml) or LPS (0 or 1 μg/ml) to the cultures for 60 minutes. Cell extracts were then subjected to SDS-PAGE Western blot analysis with antibodies specific for total and phosphorylated rpS6 (Ser240/244), 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1), and actin. Representative Western blots show inhibitory effects of rapamycin on (A) PAM- or (B) LPS-induced rpS6 phosphorylation, and the appearance of shifted 4E-BP1 γ isoform. Representative Western blots are shown, as well as densitometry determinations (mean ± SEM) of phosphorylated rpS6 (Ser240/244) from three independent experiments. Mean ± SEM, n = 3, **P < 0.01 compared to control, or +P < 0.05 compared to cells treated with PAM or LPS.