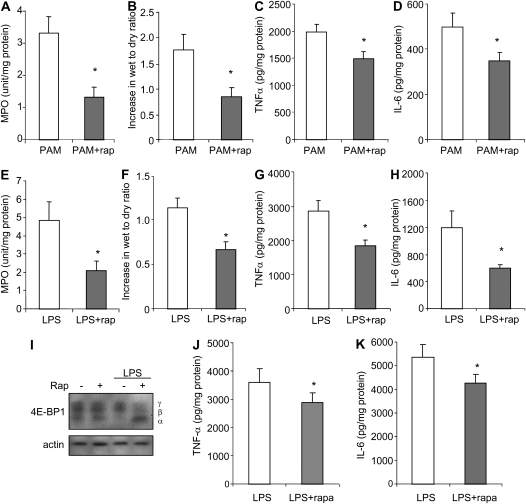
Figure 7.
Rapamycin attenuates PAM- or LPS-induced ALI in vivo. Mice were pretreated with saline or saline plus rapamycin (5 mg/kg, intraperitoneal). After 24 hours, the mice received a second injection of rapamycin or saline, followed by intratracheal administration of either PAM (10 mg/kg) or LPS (1 mg/kg). Lungs were collected 4 or 24 hours after PAM or LPS administration. (A–D) Effects of rapamycin treatment on PAM-induced increases in lung wet-to-dry ratios, lung myeloperoxidase (MPO) levels, and TNF-α and IL-6 levels in whole-lung homogenates at 24 hours. (E–H) Effects of rapamycin treatment on LPS-induced increases in lung wet-to-dry ratios, lung MPO levels, and TNF-α and IL-6 levels in whole-lung homogenate at 24 hours. (I–K) Rapamycin treatment abrogates LPS-induced 4E-BP1 γ expression and diminishes TNF-α and IL-6 levels in whole-lung homogenates at 4 hours after LPS administration. (I) Whole-lung extracts were subjected to SDS-PAGE Western blot analysis with antibodies specific for 4E-BP1 and actin. Means (±SEM) are shown (n = 6 mice per group; *P < 0.05 when compared the rapamycin/LPS or PAM group to mice treated with saline/LPS or PAM).