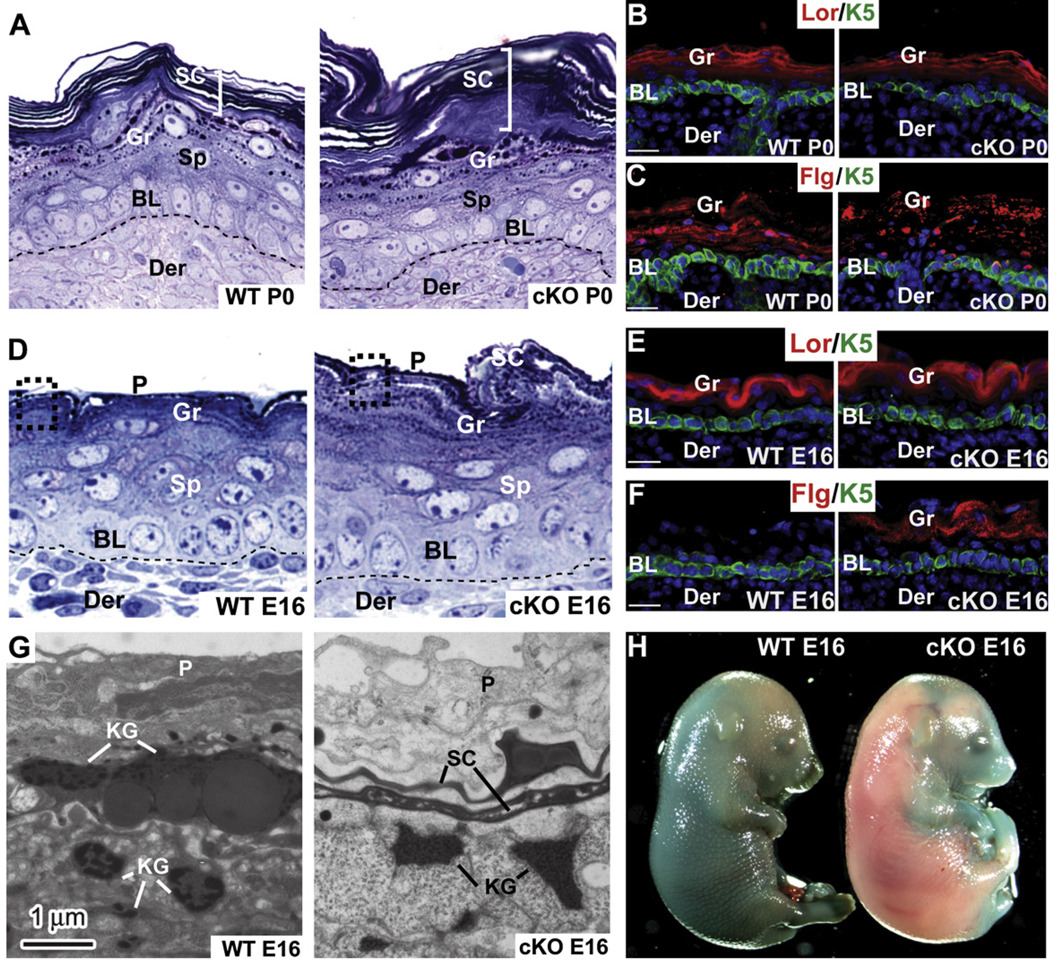
Figure 4. A Role for Ezh2 in Regulating Temporal Differentiation and Epidermal Barrier Acquisition during Skin Development.
(A–F) Histological and immunofluorescence microscopy reveals signs of accelerated epidermal differentiation in P0 and E16 Ezh2 cKO epidermis. Semithin sections in (A) and (D) are toluidine blue stained. Frozen sections are labeled with Abs as indicated (color coding according to secondary Abs).
(G) Ultrastructural analyses. Note the presence of mature keratohyalin granules (KG), a thin stratum corneum layer (SC), and a partial loss of periderm (P) in Ezh2 cKO E16 epidermis, all lacking in the WT counterpart.
(H) Blue dye exclusion assay to measure skin barrier.
Lor, Loricrin. Flg, filaggrin. BL, basal layer. Sp, spinous layer. Gr, granular layer. Der, dermis. Scale bar, 30 µm.