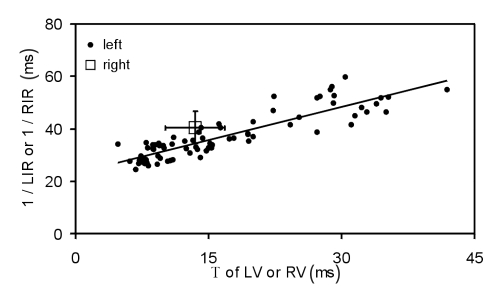
Figure 8).
Linear relation between the parameters of left (LV) and right ventricular (RV) relaxation processes. Regardless of the respective ventricular loading condition, the inverse left (1/LIR) and right indexes of relaxation (1/RIR) were plotted versus the time constant of early relaxation of ventricular pressure (T) of the LV or RV. LV data were fitted to a linear function (r2=0.8, P<0.001). The slope of the linear regression is a dimensionless, LV preload (LVPL) and LV afterload (LVAL)-independent characteristic measure of LV function. RV data entered into the graph coincided with the line of regression for LV data. However, because RV data accumulated within a circumscribed area, the latter are represented by the crossed bars (mean ± SEM). Thus, the coexistence of similar and divergent properties of LV and RV relaxation are shown (n=5 at all ALs, except n=7 for AL of 25 cm H2O)