Fig 4.
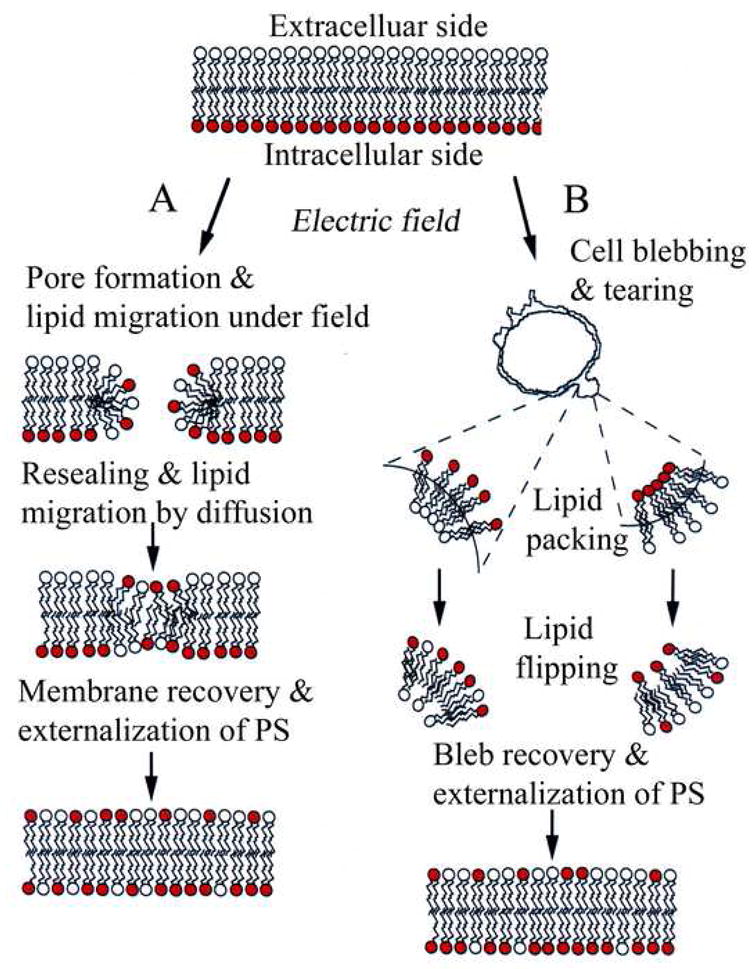
Schematic for electric field induced PS (red head group) externalization. Pathway-A: Lipid inversion could occur either through field driven transport of the negatively charged PS and/or via PS diffusion along the walls of hydrophilic membrane pores. Pathway-B: Electroporation leads to bleb formation similar to those shown in Fig. 2B. The bleb geometry constrains lipid packing due to curvature, thus favoring the scrambling of the inner and out lipid leaflets resulting in PS exposure. Exposed PS diffuses along the outer membrane periphery and remains exposed for extended time till bleb retraction and eventual sequestration to the cytoplasmic side.
