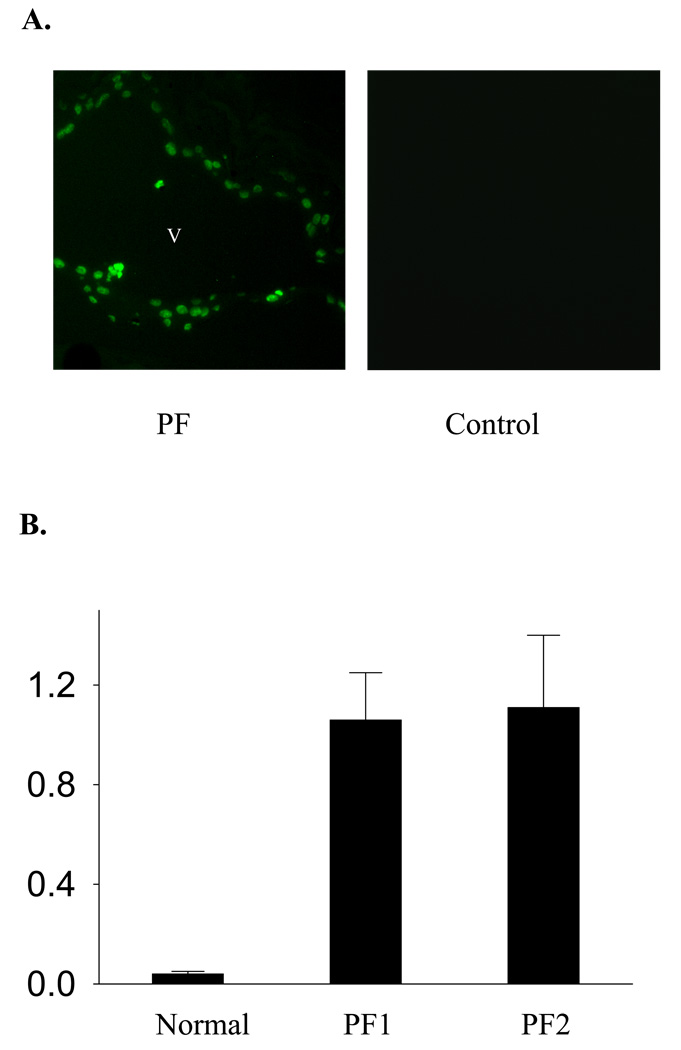
Figure 1. Induction of DNA fragmentation in the mouse epidermal cells following PF IgG passive transfer.
(A) TUNEL staining. Neonatal mice were injected (s.c.) with pathogenic PF or normal human IgG. Skin samples were obtained 20 h post IgG injections and subjected to TUNEL staining. Positive TUNEL labeling was revealed in the epidermis from mice (n=6) injected with IgG from PF1 or PF2, but not from control mice (n=3) injected with the normal human IgG. Representative results are shown. v: vesicle. (B) Oligonucleosome releasing assay. DNA oligonucleosomes presented in the cytoplasmic fractions of mouse epidermal sheets obtained from control mice (n=2) and PF mice (n=2) were analyzed with an ELISA-based assay for presence of the histone-DNA complex.