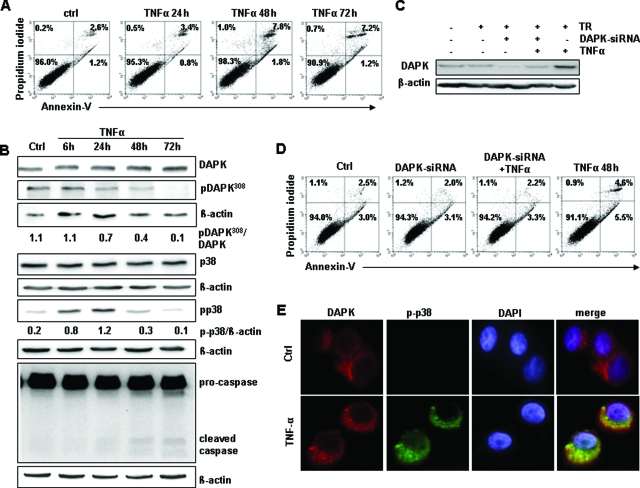
Figure 7.
TNFα induced DAPK-mediated apoptosis and DAPK/p38 co-localization in HT29 p53 mutant cells. A: Annexin-V measurements of control HT29 cells (ctrl) and HT29 cells subjected to TNFα. B: Lysates of HT29 cells subjected to TNFα were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-DAPK, anti-pDAPK308, anti-p38, anti-p-p38, anti- anti-Caspase3, or anti-β-actin. Untreated HT29 cells (ctrl) served as control. C: Lysates of HT29 cells knocked down for DAPK and subsequently subjected to TNFα for 48 hours were analyzed by anti-DAPK or anti-β-actin Western blotting. HT29 cells subjected to transfection reagent (TR), DAPK-siRNA, and TNFα-treatment served as controls. D: HT29 cells transfected with DAPK-siRNA, stimulated with TNFα were analyzed by Annexin-V assay. Untreated HT29 cells (ctrl), transfected HT29 cells (DAPK-siRNA), and TNFα-exposed HT29 cells (TNFα 48 hours) and the transfection reagent (TR) served as controls. E: TNFα-induced co-localization of DAPK and p-p38 in HT29 cells after 6 hours was determined by fluorescence immunolabeling analysis using anti-DAPK, anti-p-p38, and DAPI.