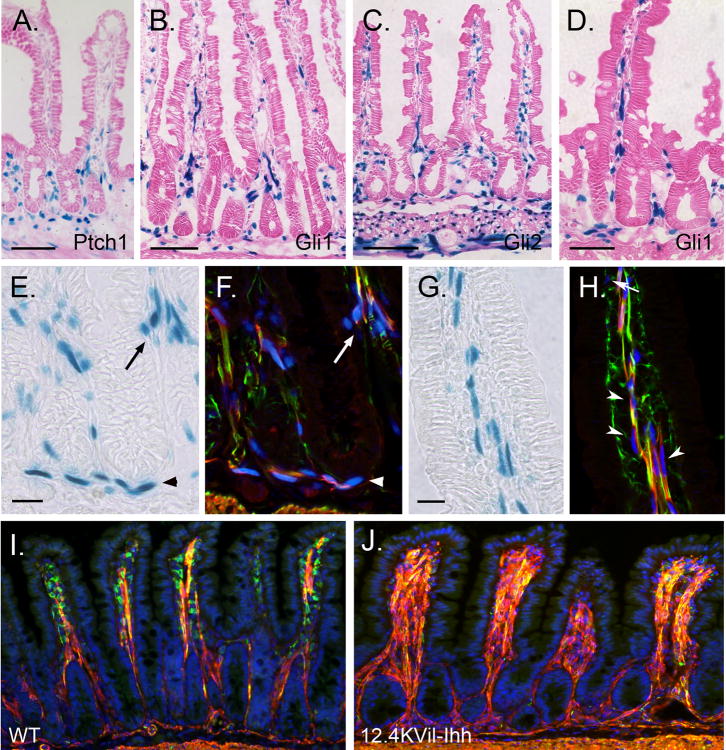
Figure 7. Hedgehog controls smooth muscle development in postnatal mice.
X-gal staining of jejunum from adult Ptch1 LacZ/+ (A), Gli1 LacZ/+ (B,D-J), and Gli2 LacZ/+ (C) mice. (A-D) Hh responsive cells are located within villus cores, at the crypt villus junction, in the submucosa and in the muscularis externa. (E-H) Sections were stained with X-gal (E,G) and then co-stained with antibodies against α-SMA (red) and desmin (green). Immunostained images taken on the confocal were overlaid (F,H) with images of the same field taken under bright field illumination (X-gal pattern, E,G). Hh responsive cells included desmin and α-SMA double positive smooth muscle cells (yellow) in the villus cores (arrowheads in H), at the crypt villus junction (arrows in E,F) and in the MM (arrowheads in E,F). Gli1 expressing cells are also detected among the desmin positive, α-SMA negative muscle precursors (green) located inside the villi close to the epithelium (arrow in H) and among the α-SMA positive, desmin negative (red) subepithelial myofibroblasts that line the crypts (not shown). (I,J) One month old wild type (WT) mice (I) and their littermates transgenic for 12.4KVil-Ihh (J). Transgenic animals show dramatic increase in villus smooth muscle and reduced smooth muscle precursors. Scale bars: (A-C, I,J) = 100μm; (D) = 50μm; (E-H) = 20μm.