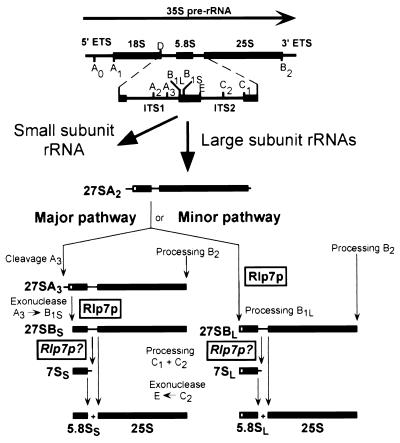
Figure 1.
The pre-rRNA processing pathway in S. cerevisiae. Yeast pre-rRNA is synthesized as a 35S primary transcript that gets cleaved and trimmed at several sites to produce the mature 18S, 5.8S, and 25S rRNAs of the ribosome. Pre-rRNA processing results in a number of recognizable pre-rRNA processing intermediates. The first processing steps occur in the 5′ portion of the 35S RNA and lead to the production of precursors to the small ribosomal subunit RNA; these processing reactions in turn release the 27SA2 precursor, which will produce the large ribosomal subunit RNAs. The 27SA2 precursor can enter two different pathways to generate the mature 5.8S and 25S rRNAs. Processing through the major pathway is initiated by RNase MRP cleavage at the A3 site, and the 27SA3 RNA gets further trimmed by 5′ to 3′ exonucleases; this exonucleolytic reaction extends to the 5′ end of the 27SBS precursor (site B1S), which is also the 5′ end of mature 5.8SS rRNA. Processing of the 27SA2 precursor through the minor pathway may also be initiated by 5′ to 3′ exonucleolytic enzyme(s); this reaction extends to site B1L and generates the 5′ end of the 27SBL, which is the mature 5′ end of 5.8SL rRNA. In both the major and minor pathways, endonucleolytic cleavages in ITS2 generate the mature 5′ end of 25S rRNA and the 7S precursors that get trimmed by 3′ to 5′ exonucleases to produce the mature 3′ end of 5.8S rRNAs. This figure has been adapted from Kressler et al. (5).