An overview of the functions and sites of action of MYST complexes throughout the yeast genome.
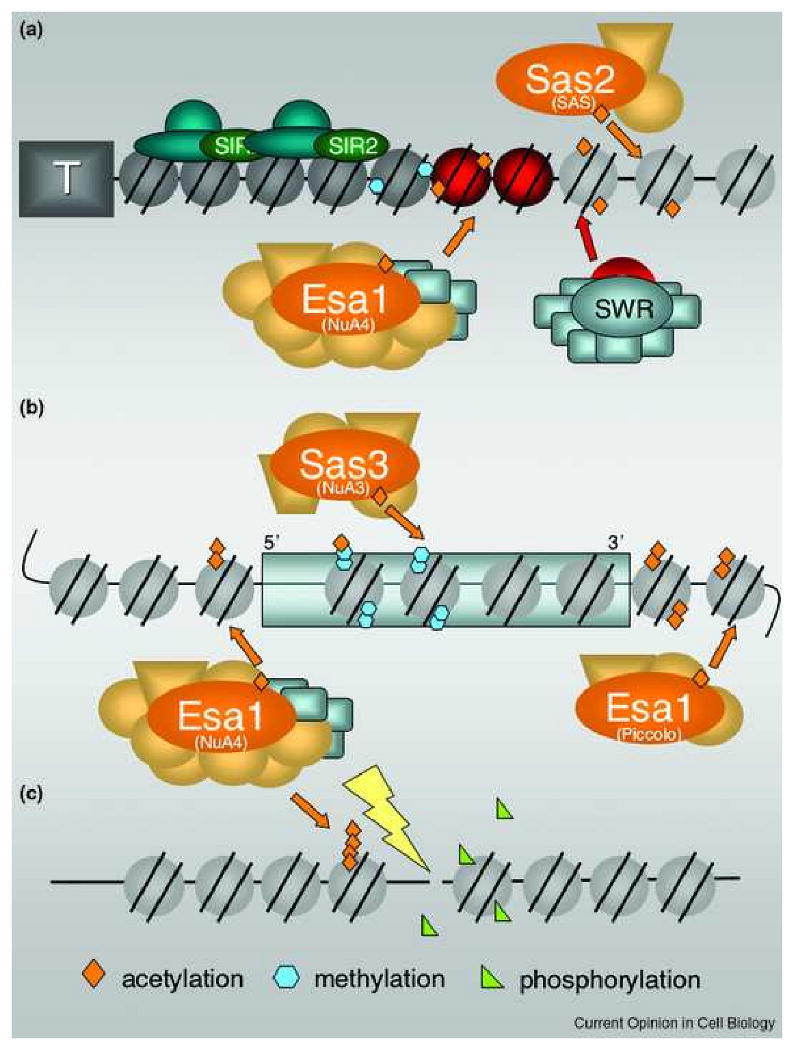
A. Boundary Functions. At subtelomeric regions, the Sas2 MYST of the SAS complex acetylates H4-K16, thereby facilitating the SWR complex's assembly of H2A.Z-containing nucleosomes (red). H2A.Z is then acetylated by the Esa1 MYST, shown here in the context of the large NuA4 complex, which has four of the same subunits found in SWR. These events facilitate formation of heterochromatin (dark nucleosomes): euchromatin (light nucleosomes) boundaries and prevent the spread of silencing proteins such as the SIR complex (blue and green), that inchudes the Sir2 deacetylase (green). Methylation of H3 by Dot1 and Set1 (complexes not shown) is also important in boundary formation. Not depicted here, but recent studies demonstrate that H2A.Z and Set1 act in concert throughout the genome, not just at subtelomeric regions, to restrict the spread of silent chromatin (see text). B. Transcriptional Control. Acetylation by Sas3 and Esa1 occurs throughout the genome. As part of NuA4, Esa1 targets 5′ regions of genes, often sites of decreased nucleosome density. This acetylation can be important for their transcriptional activation. NuA3 also mediates transcription and targets many of the same target genes as Gcn5 (not shown). For Sas3 to acetylate H3-K14, methylation by Set1 and Set2 (not shown) must occur to facilitate targeting of NuA3 by its PHD finger component Yng1. Esa1 also acetylates much of the genome through its very active, smaller Piccolo complex. C. DNA Damage Repair. At sites of DNA damage, acetylation by Esa1 and NuA4 are required for repair to occur. Cycles of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of H4 and H2A, along with the INO remodeling complex (not shown) are also important in mediating repair and recruitment of NuA4.
