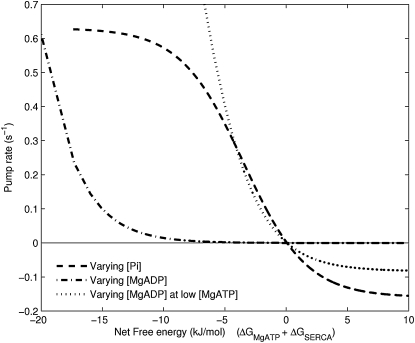
Figure 9.
The SERCA model predicts a reversal point when the net free energy is zero. However, the rate at which the pump reverses is a function of the model parameters. In the figure above, the free energy of ATP hydrolysis is reduced by increasing either [Pi] or [MgADP]. Increasing [Pi] causes the pump to reverse at an appreciable rate beyond the reversal point. However, increasing [MgADP] results in the pump slowing down considerably as it passes through the reversal point. [MgATP] = 5 mM for both curves. But when [MgADP] is increased while keeping [MgATP] low (10 μM), there is an appreciable reversal rate because the inhibitory effect of MgATP binding is reduced. Other conditions in the simulation: pH = 7, [Ca2+]i = 1 μM, [Ca2+]sr = 2 mM.