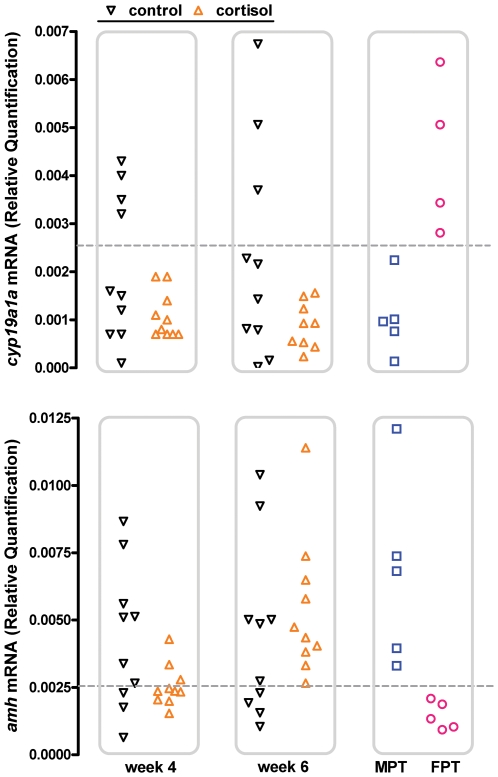
Figure 2. Abundance of mRNA transcripts of the sex differentiation genes amh and cyp19a1a in cortisol-treated (0.8 mg/g food) larvae at 4 and 6 wah.
Typical values obtained at masculinizing (MPT; 7 wah) and feminizing (FPT; 6 wah) temperatures are shown for comparison. Symbols represent individual values for 10 larvae each in control and cortisol-treated groups and 5 larvae each in the MPT and FPT. Values were normalized by the respective values of β-actin. Horizontal dotted lines represent threshold values (mean±2SD) for cyp19a1a (0.00258) and amh (0.00247) that were calculated using values from the MPT and FPT, respectively. Cortisol-treated animals showed consistent cyp19a1a downregulation and amh upregulation comparable to the typical molecular signature of masculinization of animals at the MPT whereas controls showed a bimodal distribution of mRNA transcripts that agreed with the sex ratio of 69.2% males (that is, 6–7 and 3–4 out of 10 individuals resembled those at the MPT and FPT, respectively).