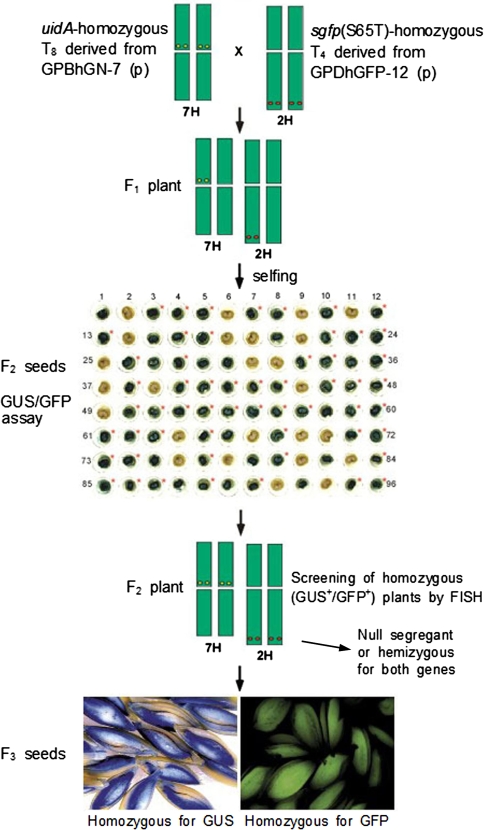
Fig. 1.
Screening of homozygous plants using GUS/GFP assay and FISH from crossed transgenic barley plants. F1 seeds were obtained from the cross of two parental plants, a homozygous T8 plant derived from GPBhGN-7 and a homozygous T4 plant derived from GPDhGFP-12; three F1 plants were tested for GUS/GFP activities. GFP expression in F2 seeds was performed using cross-sectioned half-seeds without immature embryos; GUS assay was then performed using the same materials. Expression of sgfp(S65T) is marked by an asterisk. Half-seeds with embryos expressing both GFP and GUS were saved and grown for next generations. Numbers indicate the seed number examined (Table 1). FISH technique was employed to screen the homozygous [uidA and sgfp(S65T)] F2 plants by direct mapping of transgenes on the chromosomes (Table 2; Fig. 3). Inserted uidA and sgfp(S65T) genes were localized on the centromeric region of chromosome 7H and on the subtelomeric region of chromosome 2H, respectively. Homozygous F3 generation seeds were obtained by analyzing segregation ratios of transgenes