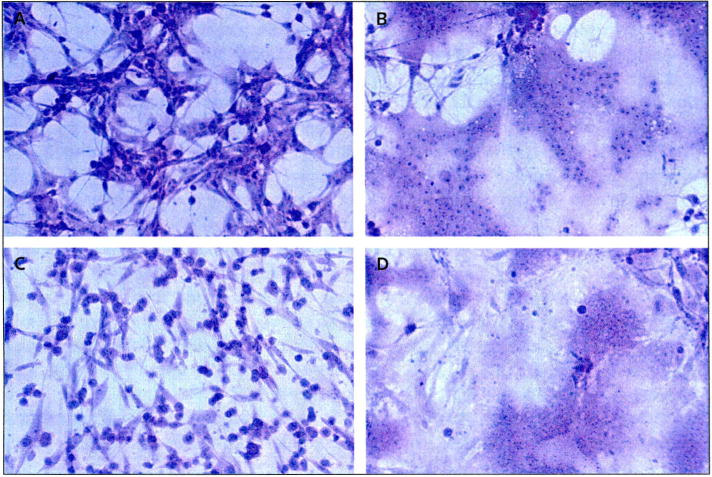
Figure 2. Prominent syncytia formation of glioma cell lines following MV-CEA infection.
Cells were stained using crystal violet stain (× 200 magnification). The human malignant glioma cell lines U87 and U118 were infected with measles virus (MV) expressing human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA; MV-CEA virus), resulting in the characteristic cytopathic effect, including extensive syncytia formation. (A) Uninfected U87 cells, (B) U87 cells 120 h after infection with MV-CEA (multiplicity of infection = 0.05), (C) uninfected U118 cells, (D) U118 cells 120 h after infection with MV-CEA (multiplicity of infection = 0.05).