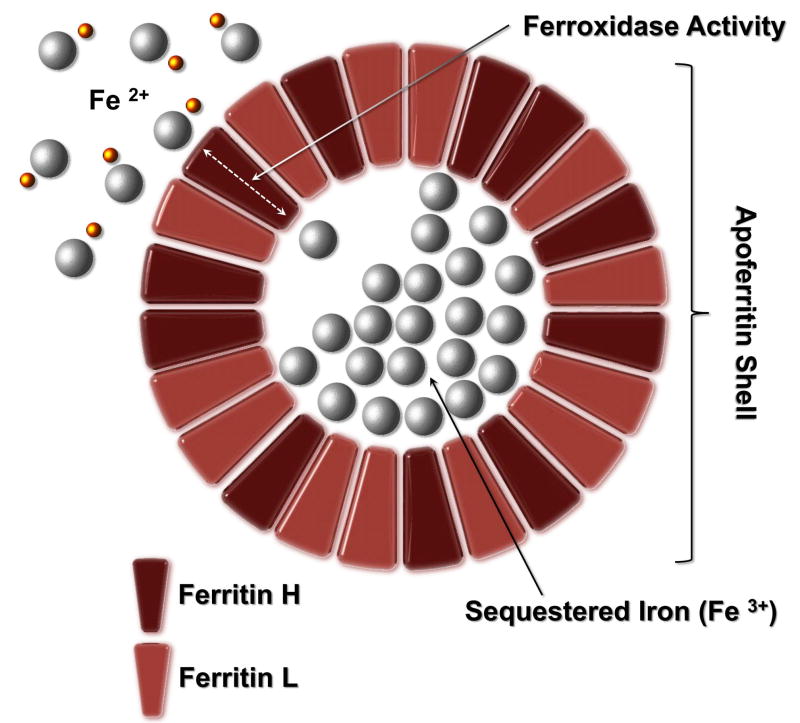
Figure 1.
Ferritin Structure: Apoferritin forms a roughly spherical container within which ferric iron is stored as a ferrihydrite mineral. Apoferritin refers to the iron-free form of the protein; the iron-containing form is termed holoferritin or simply ferritin. The apoferritin shell is composed of 24 subunits of two types, termed H and L, the ratio of which varies widely depending on tissue type and inflammation. Iron is toxic in cellular systems because of its capacity to generate reactive species (shown as yellow spheres) which can directly damage DNA and proteins.