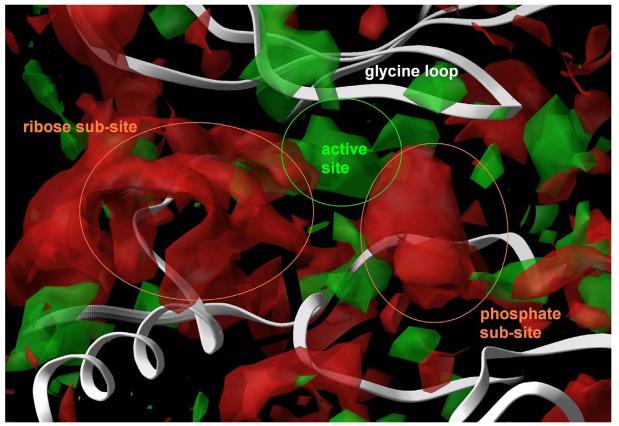
Figure 2. Superposition of crystal structures of ATP bound to monomeric CDK2 (orange) and CDK2/cyclin A (blue).
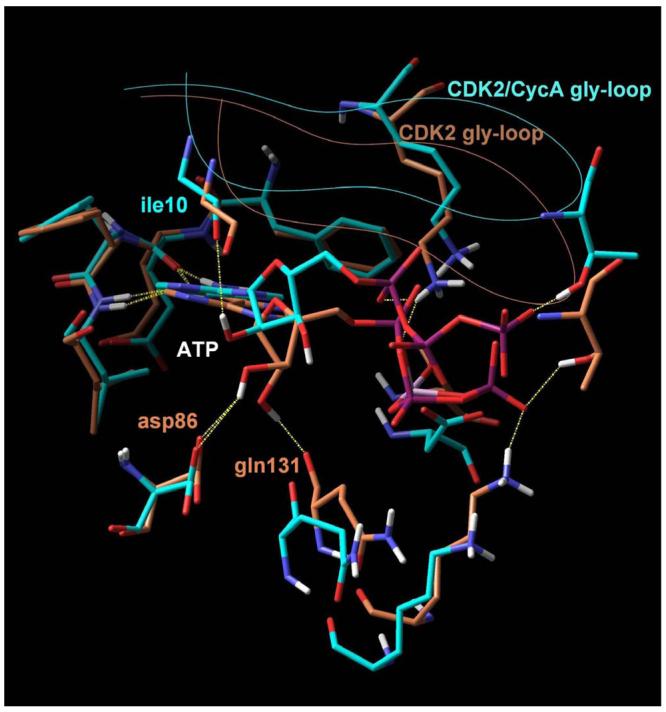
In both cases, two hydrogen bonds formed between the adenine and the receptor (yellow dashed lines) stabilize the complex. An additional set of favourable interactions exists at the ribose sub-site of the binding pocket where the sugar moiety of ATP interacts through hydrogen bonds with residues that constitute the periphery of the binding pocket, namely asp86 and gln131 in the monomeric kinase and ile10 in the CDK2/cyclin A dimer. Visible is also the Cα trace of the glycine loop at the top of the binding pocket.