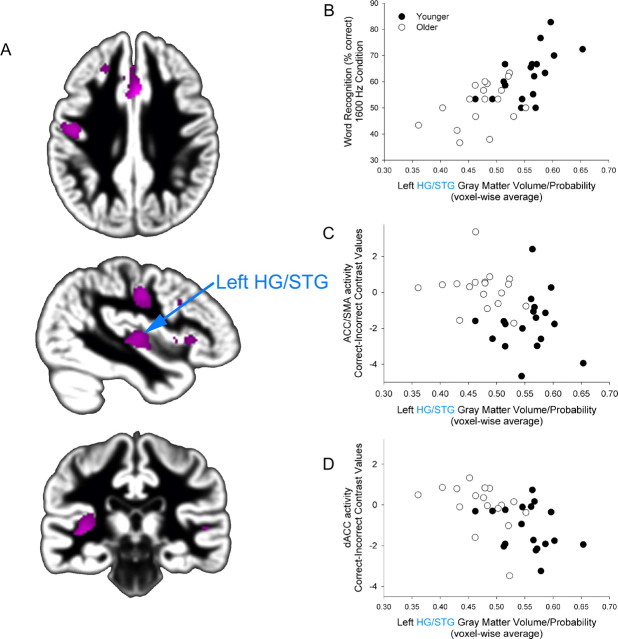
Figure 5.
Age-related differences in HG/STG gray matter volume predict word recognition performance, ACC/SMA and dACC activation. A, Younger adults exhibited greater gray matter volume than older adults (pink) within speech- and attention-related regions (as shown in Figs. 3, 4) (FDR p < 0.05). B–D, Individual variation in left medial HG/STG significantly predicts word recognition (r = 0.68, p < 0.001) (B), ACC/SMA activation [incorrect vs correct comparison (Fig. 4), r = −0.43, p < 0.01] (C), and dACC activation [incorrect vs correct comparison (Fig. 4), r = −0.56, p < 0.001] (D). The y-axis represents the average SPM correct–incorrect contrast value from the ACC/SMA cluster (C) and dACC cluster (D).