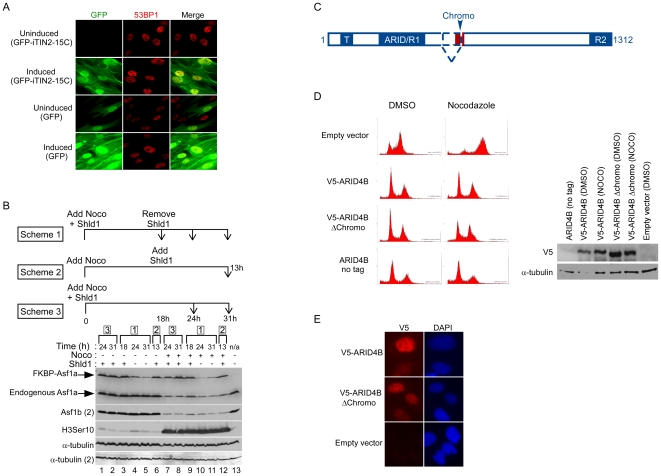
Figure 8. Functional studies using the viral vectors.
(A) Inducible expression of GFP-TIN2-15C results in induction of DNA damage. GFP or GFP-iTIN2-15C were cloned into the pLenti CMV/TO Puro vector and transduced in HCA2 T-REx cells. Following a 96 h exposure to 0.1 ug/ml tetracycline, protein induction was monitored by GFP fluorescence and the presence of DNA damage was monitored by staining for 53BP1 foci. (B) Inducible expression or depletion of Asf1a in cells arrested in mitosis using the FKBP-DD system. Three experimental schemes are depicted with the corresponding lanes indicated by brackets. Lanes 1–6: Cells were treated with DMSO as a negative control. Lanes 7–12: Nocodazole treated cells. Lane 13: untreated cells. (C) Functional domains of the ARID4B protein. ARID4B is an 1312 amino acid protein with a Tudor domain (T) at its N-terminus, two repression domains ARID/R1 and R2 [74], and a chromo domain (shown in red). Two splice isoforms have been described and the chromo domain is spliced out in the shorter isoform. (D) The chromo domain of ARID4B is not required for G1-induced growth arrest. U2OS cells were transduced with either an untagged, V5-tagged or V5-tagged minus chromo version of ARID4B recombined in the pQCXP Destination vector. An empty vector was used as a negative control. G1 arrest was monitored by incubating the cells with nocodazole as described in Materials and Methods. The ARID4B Δchromo can still induce a G1 arrest indicating that the chromo domain is not required. On the right is shown the Western blot from the same experiment to monitor expression of each construct. (E) Localization of ARID4B and ARID4B Δchromo to the cell nucleus. The V5-tagged ARID4B isoforms were detected by indirect immunofluorescence using the V5 antibody and an anti-mouse Cy5 secondary antibody. Both isoforms are detected in the nucleus of U2OS cells.