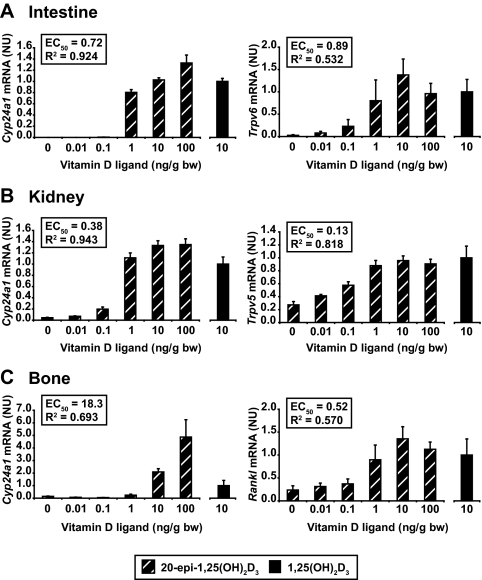
Figure 3.
1,25(OH)2D3 and 20-epi-1,25(OH)2D3 induce similar levels of gene expression. C57BL6 mice were treated with increasing concentrations of 1,25(OH)2D3 (10 ng/g bw) or 20-epi-1,25(OH)2D3 (0–100 ng/g bw) and the duodenum (A), kidney (B), or bone (calvarium) (C) isolated 6 h after injection. Total RNA was isolated, reverse transcribed, and then subjected to qPCR analysis. mRNA levels for each gene were normalized to β-actin expression. Cyp24a1, Trpv6 (a calcium transport gene), Cad9k (the calcium binding protein calbindin D9K), and cldn2 (a channel protein involved in paracellular calcium transport) were examined in the intestine. Cyp24a1, Trpv6, Trpv5 (a calcium transport gene), and Cyp27b1 (the gene responsible for the production of 1,25(OH)2D3 and suppressed by its hormonal product) were examined in the kidney. Cyp24a1, Rankl (a tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-like factor involved in vitamin D-induced calcium mobilization from bone), Vdr (a key component that mediates the actions of 1,25(OH)2D3), and Lrp5 (a costimulatory receptor in bone that is involved in Wnt activation of osteoblast differentiation) were examined in bone. Each point represents the average ± se, n = 4 or 5. Levels of gene induction at a concentrations of 10 ng/g bw for both 1,25(OH)2D3 and 20-epi-1,25(OH)2D3 were not statistically different. These data are representative of several similar experiments. NU, Normalized units.