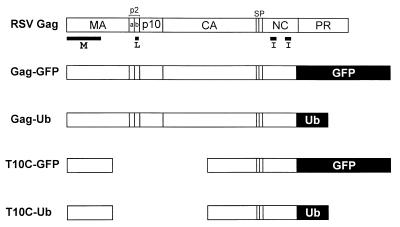
Figure 1.
RSV Gag derivatives used in this study. The wild-type polyprotein is shown at the top and its proteolytic cleavage products are indicated. The domains required for budding are indicated below Gag. The M domain mediates the binding of Gag to the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane. The I domains provide the major regions of interaction among the 1,500 molecules that create a virion particle. The L domain is required for the virus–cell separation steps that occur late in the budding pathway. The foreign sequences in Gag-GFP, Gag-Ub, T10C-GFP, and T10C-Ub replace the protease (PR) sequence and the last six residues of the nucleocapsid (NC) sequence.