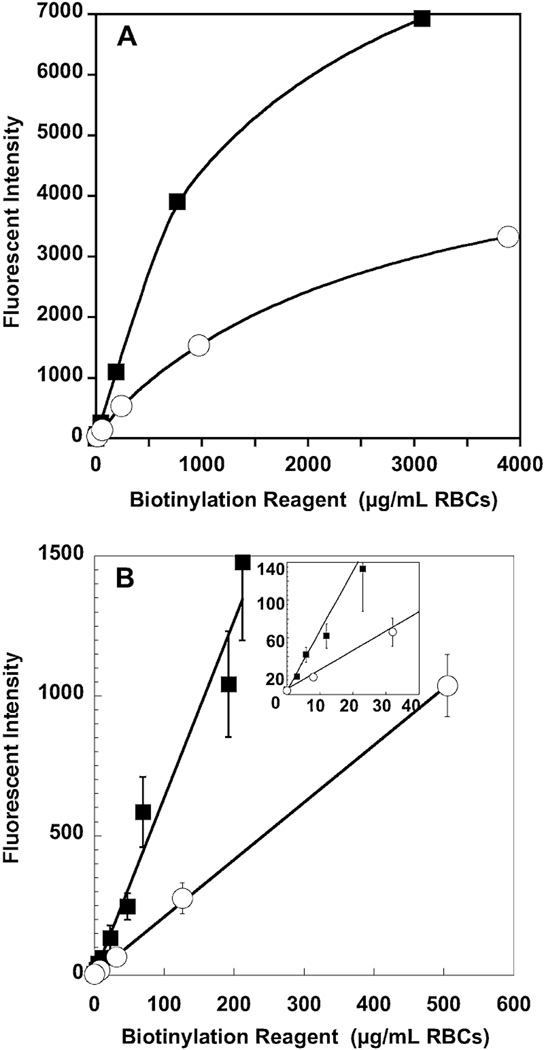
Fig. 2.
Effect of increasing concentrations of biotinylation reagent on fluorescent intensity of RBCs from human (■) and sheep (○). (A) Saturation of biotin binding sites. A study of RBCs from one human and one sheep shows evidence of saturation. (B) Relationship of biotinylation reagent in µg per mL RBCs to fluorescent intensity per RBC. There is a linear relationship between mass of sulfo-NHS-biotin and the fluorescent intensity of the biotinylated RBC for masses of 200 µg per mL or less for humans and 500 µg per mL or less for sheep. Data are depicted as mean ± 1SD.