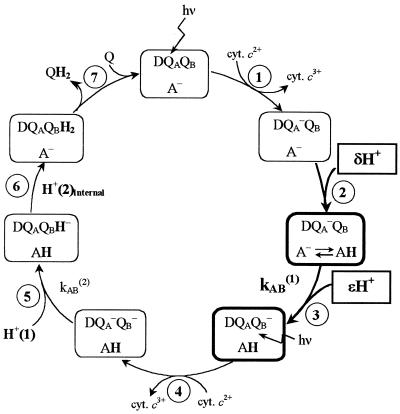
Figure 1.
The catalytic photo-cycle of quinone reduction in the RC. Electron transfer to QB occurs in two sequential reactions, kAB(1) and kAB(2) (steps 3 and 5). The transitions studied in this work are in bold. In transition 1 the donor bacterio-chlorophyll (D+) is excited by light and transfers an electron to QA. D+ is reduced by cytochrome c2. In step 2 a fraction (δ) of a proton is taken up in the D+QA− state by the amino acid (or cluster of amino acids) A. At pH > 8, A is predominantly Glu-L212. In step 3 the electron on QA is transferred to QB (kAB(1)), concomitant with additional fractional proton uptake (ɛ). In step 4 there is a second light-excited electron transfer from D to QA that involves several steps as in step 1. In step 5 the second electron transfer from QA− to QB (kAB(2)) takes place. kAB(2) is coupled to the uptake of H+(1) to the QB headgroup. In step 6, the second proton, H+(2), is transferred internally (from Glu-L212) to QB forming quinol, which in step 7 dissociates from the RC. A second quinone binds, completing the cycle.